Part C: Billing and Insurance Claims - Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Document: Part C Analysis
Pattern: Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Module: Billing and Insurance Processing System
Author: Ishara Lakshitha
Table of Contents
1. Overview & Problem Statement
Healthcare Domain Problems Addressed
Problem 1: Complex Billing Workflow
- Medical billing involves multiple sequential processing steps
- Each step has specific validation rules and business logic
- Need flexible pipeline that can handle various billing scenarios
- Different types of bills may require different processing paths
Problem 2: Insurance Claim Processing Complexity
- Insurance processing depends on patient coverage details
- Multiple insurance plans with different coverage percentages
- Need to calculate patient responsibility after insurance payments
- Complex rules for co-pays, deductibles, and coverage limits
Problem 3: Extensible Processing Pipeline
- Healthcare regulations change frequently requiring new processing steps
- Need ability to add/remove processing handlers without affecting existing code
- Different healthcare providers may have different billing workflows
- Must maintain audit trail throughout the entire process
Solution Approach
The Chain of Responsibility Pattern creates a flexible processing pipeline where each handler specializes in one aspect of billing:
- ValidationHandler: Ensures bill data integrity and basic validation
- InsuranceHandler: Processes insurance claims and calculates coverage
- FinalBillingHandler: Determines final amounts and persists to database
2. Chain of Responsibility Implementation
2.1 Pattern Participants
Handler Interface
/**
* The Handler interface declares a method for building the chain of handlers.
* It also declares a method for executing a request.
*/
public interface BillingHandler {
/**
* Sets the next handler in the chain.
* @param next The next handler to be called.
*/
void setNext(BillingHandler next);
/**
* Processes the given medical bill.
* @param request The bill processing request containing bill and patient data.
* @return true if the processing can continue, false if the chain should stop.
*/
boolean processBill(BillProcessingRequest request);
}
Request Object
/**
* Encapsulates all data needed for bill processing through the chain
*/
public class BillProcessingRequest {
private final MedicalBill bill;
private final PatientRecord patient;
public BillProcessingRequest(MedicalBill bill, PatientRecord patient) {
this.bill = bill;
this.patient = patient;
}
public MedicalBill getBill() { return bill; }
public PatientRecord getPatient() { return patient; }
}
Concrete Handler 1: ValidationHandler
/**
* A concrete handler that performs basic validation on the bill.
*/
public class ValidationHandler implements BillingHandler {
private BillingHandler next;
@Override
public void setNext(BillingHandler next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public boolean processBill(BillProcessingRequest request) {
MedicalBill bill = request.getBill();
System.out.println("ValidationHandler: Checking bill for patient " + bill.getPatientId());
// Rule 1: Amount must be greater than zero
if (bill.getAmount() <= 0) {
bill.setStatus("Rejected: Invalid Amount");
bill.addLog("Validation Failed: Bill amount must be positive.");
System.out.println("Validation Failed: Amount is not positive.");
return false; // Stop the chain
}
// Rule 2: Patient ID must not be empty
if (bill.getPatientId() == null || bill.getPatientId().trim().isEmpty()) {
bill.setStatus("Rejected: Missing Patient ID");
bill.addLog("Validation Failed: Patient ID is required.");
System.out.println("Validation Failed: Patient ID is missing.");
return false; // Stop the chain
}
// If validation passes
bill.setStatus("Validated");
bill.addLog("Bill passed initial validation.");
System.out.println("Validation successful.");
// Pass to the next handler if it exists
if (next != null) {
return next.processBill(request);
}
return true; // End of this path in the chain
}
}
Concrete Handler 2: InsuranceHandler
/**
* Handles insurance claim processing and coverage calculations
*/
public class InsuranceHandler implements BillingHandler {
private BillingHandler next;
@Override
public void setNext(BillingHandler next) {
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public boolean processBill(BillProcessingRequest request) {
MedicalBill bill = request.getBill();
PatientRecord patient = request.getPatient();
InsurancePlan plan = patient.getInsurancePlan();
System.out.println("InsuranceHandler: Checking patient " + patient.getPatientId());
if (plan != null) {
// Store the insurance plan on the bill for reference
bill.setAppliedInsurancePlan(plan);
// Calculate insurance coverage
double coveragePercent = plan.getCoveragePercent();
double amountToCover = bill.getAmount() * (coveragePercent / 100.0);
// Apply insurance payment
bill.applyInsurancePayment(amountToCover);
bill.setStatus("Insurance Processed");
bill.addLog(String.format("Insurance claim processed for policy %s (%.0f%%). Covered: $%.2f",
plan.getPlanName(), coveragePercent, amountToCover));
System.out.println("Insurance processed for " + plan.getPlanName());
} else {
bill.addLog("No insurance on file. Skipping claim processing.");
System.out.println("No insurance found.");
}
// Continue to next handler
if (next != null) {
return next.processBill(request);
}
return true;
}
}
Concrete Handler 3: FinalBillingHandler
/**
* The final handler in the chain. It determines the final status
* and saves the processed bill to the database.
*/
public class FinalBillingHandler implements BillingHandler {
private BillingHandler next; // Will be null, as this is the last handler
private final BillingDAO billingDAO;
public FinalBillingHandler() {
this.billingDAO = new BillingDAO();
}
@Override
public void setNext(BillingHandler next) {
this.next = next; // Usually null for final handler
}
@Override
public boolean processBill(BillProcessingRequest request) {
MedicalBill bill = request.getBill();
System.out.println("FinalBillingHandler: Finalizing and saving bill for patient " +
bill.getPatientId());
// Calculate remaining balance after insurance
double remainingBalance = bill.getRemainingBalance();
bill.setFinalAmount(remainingBalance);
// Determine final status based on remaining balance
if (remainingBalance <= 0) {
bill.setStatus("Closed - Fully Paid");
bill.addLog("Bill is fully paid. No remaining balance.");
} else {
bill.setStatus("Opened - Pending Payment");
bill.addLog(String.format("Final balance of $%.2f due from patient.", remainingBalance));
}
System.out.println("Final bill status: " + bill.getStatus() + ". Saving to database...");
// Save the final state of the bill to the database
int billId = billingDAO.saveBill(bill);
if (billId != -1) {
bill.setBillId(billId);
bill.addLog("Bill successfully saved to database with ID: " + billId);
System.out.println("Successfully saved bill with ID: " + billId);
} else {
bill.setStatus("Error - Failed to Save");
bill.addLog("CRITICAL ERROR: Failed to save the processed bill to the database.");
System.err.println("Failed to save bill.");
return false; // Indicate failure
}
// This is the end of the chain
return true;
}
}
3. UML Class Diagrams
3.0 Comprehensive Diagram
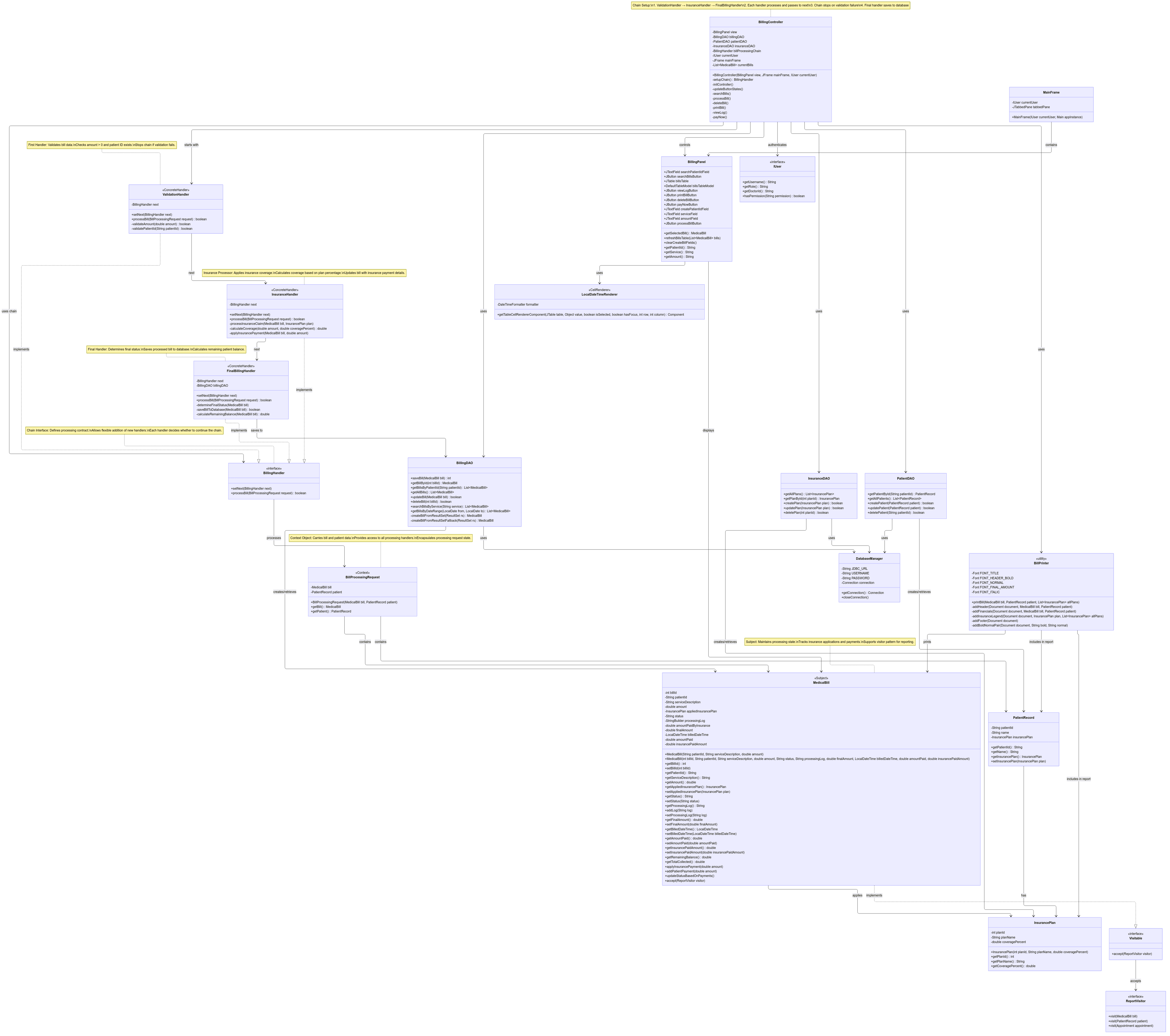
(You can find the High Res images in the Github Project Repo)
3.1 Chain of Responsibility Structure
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ <<interface>> │
│ BillingHandler │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ + setNext(next: BillingHandler) │
│ + processBill(request): boolean │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
▲
┌───────────┼───────────┐
│ │ │
┌───────────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐
│ValidationHand.│ │InsuranceHand.│ │FinalBillingHand. │
├───────────────┤ ├──────────────┤ ├──────────────────┤
│- next: Handler│ │- next: Handler│ │- next: Handler │
├───────────────┤ ├──────────────┤ │- billingDAO: DAO │
│+ setNext() │ │+ setNext() │ ├──────────────────┤
│+ processBill()│ │+ processBill()│ │+ setNext() │
└───────────────┘ └──────────────┘ │+ processBill() │
└──────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ BillProcessingRequest │
│ (Request Object) │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│- bill: MedicalBill │
│- patient: PatientRecord │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│+ getBill(): MedicalBill │
│+ getPatient(): PatientRecord │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ contains
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ MedicalBill │
│ (Domain Object) │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│- billId: int │
│- patientId: String │
│- serviceDescription: String │
│- amount: double │
│- status: String │
│- processingLog: StringBuilder │
│- appliedInsurancePlan: InsurancePlan│
│- finalAmount: double │
│- amountPaid: double │
│- insurancePaidAmount: double │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│+ addLog(entry: String): void │
│+ applyInsurancePayment(amt): void │
│+ getRemainingBalance(): double │
│+ setStatus(status: String): void │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
3.2 Chain Setup and Execution Flow
BillingController
│
▼
setupChain()
│
├─→ ValidationHandler ─→ InsuranceHandler ─→ FinalBillingHandler
│ │
└─────────────────── billProcessingChain ─────────────┘
│
▼
processBill(request)
│
┌─────────────┼─────────────┐
│ │ │
Validate Process Finalize
│ Insurance │
▼ │ ▼
Continue/Stop ▼ Save to DB
Continue Return Result
4. Detailed Code Analysis
4.1 Chain Setup and Configuration
/**
* Controller method that sets up the processing chain
* This demonstrates the flexibility of the pattern - chains can be
* configured differently based on business requirements
*/
private BillingHandler setupChain() {
// Create handler instances
BillingHandler validationHandler = new ValidationHandler();
BillingHandler insuranceHandler = new InsuranceHandler();
BillingHandler finalBillingHandler = new FinalBillingHandler();
// Link handlers in sequence
validationHandler.setNext(insuranceHandler);
insuranceHandler.setNext(finalBillingHandler);
// Return the first handler in the chain
return validationHandler;
}
4.2 Request Processing Flow
/**
* Main processing method that initiates the chain
* The controller creates the request and starts the chain processing
*/
private void processBill() {
// Collect and validate input data
String patientId = view.getPatientId();
String service = view.getService();
String amountStr = view.getAmount();
// Retrieve patient record for insurance information
PatientRecord patient = patientDAO.getPatientById(patientId);
if (patient == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view, "Patient with ID '" + patientId + "' not found.",
"Validation Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Validate amount
double amount;
try {
amount = Double.parseDouble(amountStr);
if (amount <= 0) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view, "Amount must be greater than 0.",
"Validation Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
} catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view, "Invalid amount. Please enter a valid number.",
"Input Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Create bill and request objects
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill(patientId, service, amount);
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Start the chain processing
try {
boolean success = billProcessingChain.processBill(request);
if (success) {
// Calculate and set insurance payment information
if (bill.getAmount() > bill.getFinalAmount()) {
double insurancePayment = bill.getAmount() - bill.getFinalAmount();
bill.setInsurancePaidAmount(insurancePayment);
}
// Show success message with detailed information
showBillProcessingResults(bill);
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view, "Bill processing failed: " + bill.getStatus(),
"Processing Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view, "An error occurred during bill processing: " + e.getMessage(),
"System Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
}
4.3 Validation Logic Implementation
/**
* ValidationHandler implements comprehensive bill validation
* This handler can stop the chain if critical validation fails
*/
@Override
public boolean processBill(BillProcessingRequest request) {
MedicalBill bill = request.getBill();
System.out.println("ValidationHandler: Checking bill for patient " + bill.getPatientId());
// Rule 1: Amount validation
if (bill.getAmount() <= 0) {
bill.setStatus("Rejected: Invalid Amount");
bill.addLog("Validation Failed: Bill amount must be positive.");
System.out.println("Validation Failed: Amount is not positive.");
return false; // Stop the chain - critical error
}
// Rule 2: Patient ID validation
if (bill.getPatientId() == null || bill.getPatientId().trim().isEmpty()) {
bill.setStatus("Rejected: Missing Patient ID");
bill.addLog("Validation Failed: Patient ID is required.");
System.out.println("Validation Failed: Patient ID is missing.");
return false; // Stop the chain - critical error
}
// Additional validation rules can be added here
// Rule 3: Service description validation
if (bill.getServiceDescription() == null || bill.getServiceDescription().trim().isEmpty()) {
bill.setStatus("Rejected: Missing Service Description");
bill.addLog("Validation Failed: Service description is required.");
System.out.println("Validation Failed: Service description is missing.");
return false;
}
// All validation passed
bill.setStatus("Validated");
bill.addLog("Bill passed initial validation.");
System.out.println("Validation successful.");
// Continue to next handler
if (next != null) {
return next.processBill(request);
}
return true; // End of chain if no next handler
}
4.4 Insurance Processing Logic
/**
* InsuranceHandler calculates coverage and applies insurance payments
* This handler continues processing regardless of insurance status
*/
@Override
public boolean processBill(BillProcessingRequest request) {
MedicalBill bill = request.getBill();
PatientRecord patient = request.getPatient();
InsurancePlan plan = patient.getInsurancePlan();
System.out.println("InsuranceHandler: Checking patient " + patient.getPatientId());
if (plan != null) {
// Store insurance plan reference on the bill
bill.setAppliedInsurancePlan(plan);
// Calculate coverage amount
double coveragePercent = plan.getCoveragePercent();
double amountToCover = bill.getAmount() * (coveragePercent / 100.0);
// Apply the insurance payment
bill.applyInsurancePayment(amountToCover);
bill.setStatus("Insurance Processed");
bill.addLog(String.format("Insurance claim processed for policy %s (%.0f%%). Covered: $%.2f",
plan.getPlanName(), coveragePercent, amountToCover));
System.out.println("Insurance processed for " + plan.getPlanName());
} else {
// No insurance - log and continue
bill.addLog("No insurance on file. Skipping claim processing.");
System.out.println("No insurance found.");
}
// Always continue to next handler (insurance is optional)
if (next != null) {
return next.processBill(request);
}
return true;
}
4.5 Final Processing and Persistence
/**
* FinalBillingHandler determines final amounts and persists to database
* This is the terminal handler that completes the processing workflow
*/
@Override
public boolean processBill(BillProcessingRequest request) {
MedicalBill bill = request.getBill();
System.out.println("FinalBillingHandler: Finalizing and saving bill for patient " +
bill.getPatientId());
// Calculate what the patient owes after insurance
double remainingBalance = bill.getRemainingBalance();
bill.setFinalAmount(remainingBalance);
// Set final status based on remaining balance
if (remainingBalance <= 0) {
bill.setStatus("Closed - Fully Paid");
bill.addLog("Bill is fully paid. No remaining balance.");
} else {
bill.setStatus("Opened - Pending Payment");
bill.addLog(String.format("Final balance of $%.2f due from patient.", remainingBalance));
}
System.out.println("Final bill status: " + bill.getStatus() + ". Saving to database...");
// Persist to database
int billId = billingDAO.saveBill(bill);
if (billId != -1) {
bill.setBillId(billId);
bill.addLog("Bill successfully saved to database with ID: " + billId);
System.out.println("Successfully saved bill with ID: " + billId);
return true; // Success
} else {
bill.setStatus("Error - Failed to Save");
bill.addLog("CRITICAL ERROR: Failed to save the processed bill to the database.");
System.err.println("Failed to save bill.");
return false; // Indicate failure
}
}
5. Multi-Step Processing Workflow
5.1 Complete Processing Sequence
/**
* Example of a complete bill processing workflow
* This demonstrates how the chain handles a typical billing scenario
*/
public void demonstrateCompleteWorkflow() {
// Step 1: Create initial bill
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Annual Checkup", 200.00);
// Step 2: Retrieve patient with insurance information
PatientRecord patient = patientDAO.getPatientById("P001");
// Assume patient has 80% coverage insurance plan
// Step 3: Create processing request
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Step 4: Execute chain processing
boolean success = billProcessingChain.processBill(request);
// Expected results after processing:
// - bill.getAmount() = 200.00 (original amount)
// - bill.getInsurancePaidAmount() = 160.00 (80% coverage)
// - bill.getFinalAmount() = 40.00 (patient responsibility)
// - bill.getStatus() = "Opened - Pending Payment"
// - bill.getBillId() > 0 (assigned by database)
}
5.2 Error Handling and Chain Termination
/**
* Example showing how validation errors terminate the chain
*/
public void demonstrateValidationFailure() {
// Create invalid bill (negative amount)
MedicalBill invalidBill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Invalid Service", -50.00);
PatientRecord patient = patientDAO.getPatientById("P001");
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(invalidBill, patient);
// Processing will stop at ValidationHandler
boolean success = billProcessingChain.processBill(request);
// Expected results:
// - success = false
// - bill.getStatus() = "Rejected: Invalid Amount"
// - InsuranceHandler and FinalBillingHandler never executed
// - No database persistence occurs
}
5.3 Insurance Coverage Scenarios
/**
* Different insurance scenarios handled by the chain
*/
public void demonstrateInsuranceScenarios() {
// Scenario 1: Patient with 100% coverage
MedicalBill bill1 = new MedicalBill("P001", "Covered Service", 100.00);
// After processing: finalAmount = 0.00, status = "Closed - Fully Paid"
// Scenario 2: Patient with no insurance
MedicalBill bill2 = new MedicalBill("P002", "Self-Pay Service", 150.00);
// After processing: finalAmount = 150.00, status = "Opened - Pending Payment"
// Scenario 3: Patient with partial coverage
MedicalBill bill3 = new MedicalBill("P003", "Partial Coverage", 300.00);
// 70% coverage: finalAmount = 90.00, status = "Opened - Pending Payment"
}
6. Usage Scenarios
6.1 Scenario 1: Standard Insurance Claim Processing
// Setup: Patient with 80% insurance coverage
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "John Doe");
InsurancePlan plan = new InsurancePlan(1, "Blue Cross", 80.0);
patient.setInsurancePlan(plan);
// Create bill for $500 medical service
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P001", "MRI Scan", 500.00);
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Process through chain
boolean success = chain.processBill(request);
// Expected results:
// - Validation: Passed
// - Insurance: $400.00 covered (80% of $500)
// - Final: $100.00 patient responsibility
// - Status: "Opened - Pending Payment"
// - Database: Bill saved with assigned ID
6.2 Scenario 2: Validation Failure
// Create bill with invalid data
MedicalBill invalidBill = new MedicalBill("", "Service", -100.00);
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P002", "Jane Smith");
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(invalidBill, patient);
// Process through chain
boolean success = chain.processBill(request);
// Expected results:
// - success = false
// - Status: "Rejected: Missing Patient ID" (first validation failure)
// - Chain terminated at ValidationHandler
// - No insurance processing
// - No database persistence
6.3 Scenario 3: No Insurance Coverage
// Setup: Patient without insurance
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P003", "Bob Wilson");
// No insurance plan set
// Create bill
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P003", "Consultation", 150.00);
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Process through chain
boolean success = chain.processBill(request);
// Expected results:
// - Validation: Passed
// - Insurance: Skipped (no coverage)
// - Final: $150.00 patient responsibility
// - Status: "Opened - Pending Payment"
// - Database: Bill saved successfully
6.4 Scenario 4: Full Insurance Coverage
// Setup: Patient with 100% coverage
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P004", "Alice Brown");
InsurancePlan fullCoverage = new InsurancePlan(2, "Premium Plan", 100.0);
patient.setInsurancePlan(fullCoverage);
// Create bill
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P004", "Emergency Room Visit", 800.00);
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Process through chain
boolean success = chain.processBill(request);
// Expected results:
// - Validation: Passed
// - Insurance: $800.00 covered (100% of $800)
// - Final: $0.00 patient responsibility
// - Status: "Closed - Fully Paid"
// - Database: Bill saved as fully paid
7. Benefits & Trade-offs
7.1 Chain of Responsibility Benefits
Flexibility and Extensibility
- Easy to add new processing steps without modifying existing handlers
- Can reorder handlers to change processing sequence
- Different chains can be configured for different bill types
- Handlers can be reused in multiple processing workflows
Separation of Concerns
- Each handler focuses on a single responsibility
- Validation logic separated from insurance processing
- Database persistence isolated in final handler
- Clear audit trail through processing log
Loose Coupling
- Handlers don't need to know about other handlers in the chain
- Request object encapsulates all necessary data
- Easy to test individual handlers in isolation
- Reduced dependencies between processing components
Dynamic Processing Control
- Handlers can terminate the chain based on conditions
- Optional processing steps (like insurance) can be skipped gracefully
- Error handling contained within appropriate handlers
- Processing can branch based on business rules
7.2 Healthcare Domain Specific Benefits
Compliance and Audit Trail
- Complete processing log maintained throughout the chain
- Each step documented for regulatory compliance
- Clear responsibility assignment for each processing stage
- Traceable decision-making process
Business Rule Management
- Insurance rules centralized in InsuranceHandler
- Validation rules can be easily modified or extended
- Different processing rules for different insurance types
- Configurable coverage calculations
Error Recovery and Handling
- Failed validation prevents incorrect billing
- Insurance processing failures don't stop the entire workflow
- Database errors properly handled and logged
- Clear error messages for each failure type
7.3 Trade-offs and Considerations
Processing Overhead
- Additional object creation for request wrappers
- Chain traversal adds method call overhead
- Logging operations increase processing time
- Memory usage for maintaining processing logs
Debugging Complexity
- Multiple handlers make debugging more complex
- Chain execution flow can be hard to follow
- Error sources may be unclear across multiple handlers
- Testing requires careful setup of handler chains
Configuration Management
- Chain setup must be done correctly for proper operation
- Handler order is critical for correct processing
- Different environments may require different chains
- Configuration errors can lead to incorrect processing
Performance Considerations
- Chain processing is sequential, not parallel
- Database operations in final handler can become bottleneck
- Large processing logs consume memory
- Exception handling overhead across multiple handlers
8. Testing & Validation
8.1 Unit Testing Individual Handlers
@Test
public void testValidationHandlerSuccess() {
// Arrange
ValidationHandler handler = new ValidationHandler();
MedicalBill validBill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Service", 100.00);
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "Test Patient");
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(validBill, patient);
// Act
boolean result = handler.processBill(request);
// Assert
assertTrue(result);
assertEquals("Validated", validBill.getStatus());
assertTrue(validBill.getProcessingLog().contains("Bill passed initial validation"));
}
@Test
public void testValidationHandlerFailure() {
// Arrange
ValidationHandler handler = new ValidationHandler();
MedicalBill invalidBill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Service", -50.00);
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "Test Patient");
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(invalidBill, patient);
// Act
boolean result = handler.processBill(request);
// Assert
assertFalse(result);
assertEquals("Rejected: Invalid Amount", invalidBill.getStatus());
assertTrue(invalidBill.getProcessingLog().contains("Bill amount must be positive"));
}
@Test
public void testInsuranceHandlerWithCoverage() {
// Arrange
InsuranceHandler handler = new InsuranceHandler();
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Service", 200.00);
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "Test Patient");
InsurancePlan plan = new InsurancePlan(1, "Test Plan", 80.0);
patient.setInsurancePlan(plan);
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Act
boolean result = handler.processBill(request);
// Assert
assertTrue(result);
assertEquals("Insurance Processed", bill.getStatus());
assertEquals(160.00, bill.getInsurancePaidAmount(), 0.01);
assertEquals(plan, bill.getAppliedInsurancePlan());
}
@Test
public void testInsuranceHandlerWithoutCoverage() {
// Arrange
InsuranceHandler handler = new InsuranceHandler();
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Service", 200.00);
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "Test Patient");
// No insurance plan set
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Act
boolean result = handler.processBill(request);
// Assert
assertTrue(result);
assertEquals(0.00, bill.getInsurancePaidAmount(), 0.01);
assertNull(bill.getAppliedInsurancePlan());
assertTrue(bill.getProcessingLog().contains("No insurance on file"));
}
8.2 Integration Testing Chain Processing
@Test
public void testCompleteChainProcessing() {
// Arrange
BillingHandler chain = setupTestChain();
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Test Service", 300.00);
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "Test Patient");
InsurancePlan plan = new InsurancePlan(1, "Test Plan", 70.0);
patient.setInsurancePlan(plan);
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Act
boolean result = chain.processBill(request);
// Assert
assertTrue(result);
assertEquals("Opened - Pending Payment", bill.getStatus());
assertEquals(210.00, bill.getInsurancePaidAmount(), 0.01); // 70% of 300
assertEquals(90.00, bill.getFinalAmount(), 0.01); // 30% patient responsibility
assertTrue(bill.getBillId() > 0); // Assigned by database
}
@Test
public void testChainTerminationOnValidationFailure() {
// Arrange
BillingHandler chain = setupTestChain();
MedicalBill invalidBill = new MedicalBill("", "Service", 100.00); // Invalid patient ID
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "Test Patient");
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(invalidBill, patient);
// Act
boolean result = chain.processBill(request);
// Assert
assertFalse(result);
assertEquals("Rejected: Missing Patient ID", invalidBill.getStatus());
assertEquals(0.00, invalidBill.getInsurancePaidAmount(), 0.01); // Insurance not processed
assertEquals(0, invalidBill.getBillId()); // Not saved to database
}
8.3 Performance Testing
@Test
public void testChainPerformanceWithLargeBatch() {
// Arrange
BillingHandler chain = setupTestChain();
List<BillProcessingRequest> requests = createTestBatch(1000);
// Act
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int successCount = 0;
for (BillProcessingRequest request : requests) {
if (chain.processBill(request)) {
successCount++;
}
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Assert
assertEquals(1000, successCount);
assertTrue("Processing should complete within 5 seconds",
(endTime - startTime) < 5000);
}
8.4 Error Handling Testing
@Test
public void testDatabaseFailureHandling() {
// Arrange - Mock DAO to simulate database failure
BillingHandler chain = setupChainWithMockDAO();
MedicalBill bill = new MedicalBill("P001", "Service", 100.00);
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "Test Patient");
BillProcessingRequest request = new BillProcessingRequest(bill, patient);
// Configure mock to fail
when(mockBillingDAO.saveBill(any())).thenReturn(-1);
// Act
boolean result = chain.processBill(request);
// Assert
assertFalse(result);
assertEquals("Error - Failed to Save", bill.getStatus());
assertTrue(bill.getProcessingLog().contains("CRITICAL ERROR: Failed to save"));
}
Conclusion
The Chain of Responsibility pattern implementation in the billing and insurance processing system demonstrates a sophisticated approach to handling complex, multi-step workflows in healthcare software. The pattern successfully addresses the core challenges of medical billing while providing a flexible, maintainable, and extensible architecture.
Key Achievements
- Workflow Management: Successfully implements a complex billing workflow with validation, insurance processing, and persistence
- Flexibility: Easy to add new processing steps or modify existing ones without affecting other components
- Error Handling: Robust error handling with appropriate chain termination and detailed logging
- Insurance Integration: Seamless integration of insurance claim processing with configurable coverage rules
- Audit Trail: Complete processing log maintained throughout the entire workflow
- Database Integration: Clean separation between business logic and data persistence
Real-World Healthcare Impact
The Chain of Responsibility pattern proves particularly valuable in healthcare billing contexts where:
- Regulatory Compliance requires detailed audit trails and processing documentation
- Insurance Complexity demands flexible coverage calculation and claim processing
- Error Prevention is critical for accurate billing and patient satisfaction
- Workflow Flexibility allows adaptation to different healthcare provider requirements
- Integration Requirements need clean interfaces between billing, insurance, and accounting systems
Pattern Benefits Realized
The implementation successfully demonstrates how the Chain of Responsibility pattern can:
- Decouple complex processing steps while maintaining workflow integrity
- Centralize business rules within appropriate handler responsibilities
- Enable dynamic processing control with early termination capabilities
- Support extensibility for evolving healthcare regulations and requirements
- Provide clear separation between validation, processing, and persistence concerns
The billing system's chain-based architecture provides a solid foundation for handling the complexities of healthcare financial processing while maintaining the flexibility needed for future enhancements and regulatory changes.
Document Status: Part C Complete
Next: Part D - Managing Medical Staff Roles and Permissions (Decorator Pattern)