Part A: Patient Record Management - Memento & Prototype Patterns
Document: Part A Analysis
Patterns: Memento Pattern & Prototype Pattern
Module: Patient Record Management
Author: Ishara Lakshitha
Table of Contents
1. Overview & Problem Statement
Healthcare Domain Problems Addressed
Problem 1: State Management with Undo Capability
- Healthcare professionals need to modify patient records frequently
- Mistakes in patient data can have serious consequences
- Need ability to undo changes without losing data integrity
- Must maintain complete audit trail of modifications
Problem 2: Efficient Patient Record Creation
- Creating new patient records from scratch is time-consuming
- Many patients share similar baseline information
- Need template-based record creation for efficiency
- Must ensure data independence between records
Solution Approach
The implementation combines two creational/behavioral patterns:
- Memento Pattern: Captures and restores patient record state without violating encapsulation
- Prototype Pattern: Enables efficient patient record creation through cloning
2. Design Patterns Implementation
2.1 Memento Pattern Implementation
Pattern Participants
// Originator
public class PatientRecord implements Cloneable, Visitable {
// State to be saved/restored
private String name;
private List<String> medicalHistory;
private List<String> treatmentPlans;
// Memento creation
public PatientRecordMemento save() {
return new PatientRecordMemento(
this.name,
new ArrayList<>(this.medicalHistory),
new ArrayList<>(this.treatmentPlans)
);
}
// State restoration
public void restore(PatientRecordMemento memento) {
this.name = memento.getName();
this.medicalHistory = memento.getMedicalHistory();
this.treatmentPlans = memento.getTreatmentPlans();
}
}
// Memento
public final class PatientRecordMemento {
private final String name;
private final List<String> medicalHistory;
private final List<String> treatmentPlans;
public PatientRecordMemento(String name, List<String> medicalHistory,
List<String> treatmentPlans) {
this.name = name;
this.medicalHistory = new ArrayList<>(medicalHistory); // Deep copy
this.treatmentPlans = new ArrayList<>(treatmentPlans); // Deep copy
}
// Package-private getters for encapsulation
String getName() { return name; }
List<String> getMedicalHistory() { return new ArrayList<>(medicalHistory); }
List<String> getTreatmentPlans() { return new ArrayList<>(treatmentPlans); }
}
// Caretaker
public class RecordHistory {
private final Stack<PatientRecordMemento> history = new Stack<>();
private final PatientRecord patientRecord;
public void save() {
System.out.println("Saving state...");
history.push(patientRecord.save());
}
public void undo() {
if (history.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Cannot undo. No history available.");
return;
}
PatientRecordMemento lastState = history.pop();
System.out.println("Restoring to previous state...");
patientRecord.restore(lastState);
}
}
2.2 Prototype Pattern Implementation
Deep Cloning Implementation
public class PatientRecord implements Cloneable, Visitable {
@Override
public PatientRecord clone() {
try {
PatientRecord clonedRecord = (PatientRecord) super.clone();
// Perform deep copy of mutable fields
clonedRecord.medicalHistory = new ArrayList<>(this.medicalHistory);
clonedRecord.treatmentPlans = new ArrayList<>(this.treatmentPlans);
return clonedRecord;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError(); // Should not happen since we implement Cloneable
}
}
}
3. UML Class Diagrams
3.0 Comprehensive Diagram
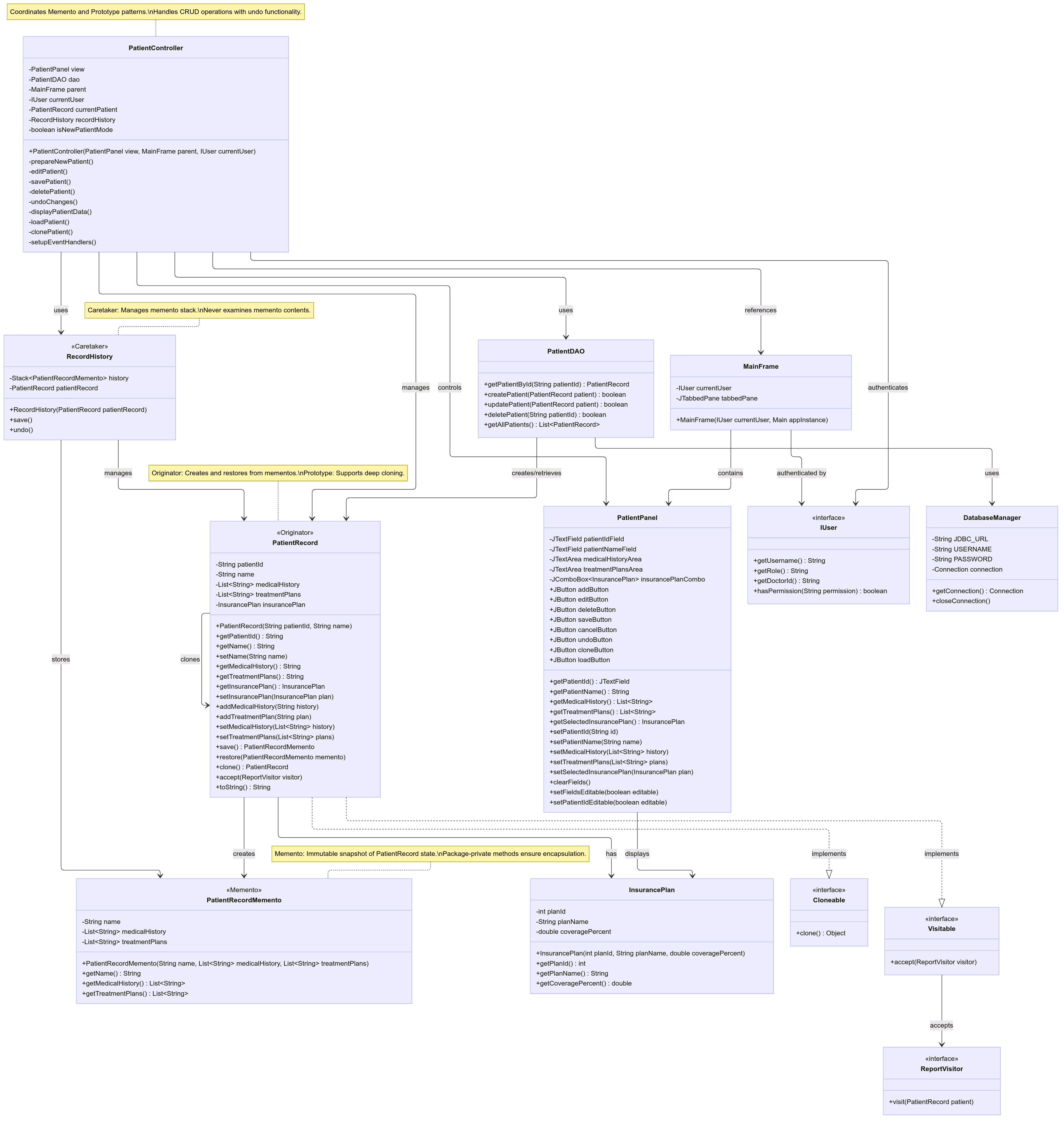
(You can find the High Res images in the Github Project Repo)
3.1 Memento Pattern Structure
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PatientRecord │
│ (Originator) │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ - name: String │
│ - medicalHistory: List<String> │
│ - treatmentPlans: List<String> │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ + save(): PatientRecordMemento │
│ + restore(memento): void │
│ + setName(name): void │
│ + addMedicalHistory(history): void │
│ + addTreatmentPlan(plan): void │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
│
│ creates
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PatientRecordMemento │
│ (Memento) │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ - name: String │
│ - medicalHistory: List<String> │
│ - treatmentPlans: List<String> │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ + getName(): String │
│ + getMedicalHistory(): List<String> │
│ + getTreatmentPlans(): List<String> │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
▲
│ stores
│
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ RecordHistory │
│ (Caretaker) │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ - history: Stack<PatientRecordMem.> │
│ - patientRecord: PatientRecord │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ + save(): void │
│ + undo(): void │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
3.2 Prototype Pattern Structure
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ <<interface>> │
│ Cloneable │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
▲
│
│ implements
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ PatientRecord │
│ (Prototype) │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ - patientId: String │
│ - name: String │
│ - medicalHistory: List<String> │
│ - treatmentPlans: List<String> │
│ - insurancePlan: InsurancePlan │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ + clone(): PatientRecord │
│ + PatientRecord(id, name) │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
4. Detailed Code Analysis
4.1 Memento Pattern Deep Dive
State Capture Mechanism
/**
* Creates a snapshot of current patient record state
* Key Design Decisions:
* 1. Deep copying of mutable collections prevents external modification
* 2. Immutable fields (patientId) are not included in memento
* 3. Only essential state for undo functionality is captured
*/
public PatientRecordMemento save() {
return new PatientRecordMemento(
this.name, // Simple field copy
new ArrayList<>(this.medicalHistory), // Deep copy for safety
new ArrayList<>(this.treatmentPlans) // Deep copy for safety
);
}
State Restoration Mechanism
/**
* Restores patient record from memento state
* Key Design Decisions:
* 1. Memento provides defensive copies to prevent external modification
* 2. Only mutable state is restored (patientId remains unchanged)
* 3. Direct assignment ensures complete state replacement
*/
public void restore(PatientRecordMemento memento) {
this.name = memento.getName(); // Direct assignment
this.medicalHistory = memento.getMedicalHistory(); // Gets defensive copy
this.treatmentPlans = memento.getTreatmentPlans(); // Gets defensive copy
}
Encapsulation Protection
public final class PatientRecordMemento {
// Package-private access ensures only PatientRecord can access state
String getName() { return name; }
// Always return defensive copies to prevent external modification
List<String> getMedicalHistory() {
return new ArrayList<>(medicalHistory);
}
List<String> getTreatmentPlans() {
return new ArrayList<>(treatmentPlans);
}
}
4.2 Prototype Pattern Deep Dive
Deep Cloning Implementation
@Override
public PatientRecord clone() {
try {
// Step 1: Perform shallow clone using Object.clone()
PatientRecord clonedRecord = (PatientRecord) super.clone();
// Step 2: Deep copy mutable reference fields
clonedRecord.medicalHistory = new ArrayList<>(this.medicalHistory);
clonedRecord.treatmentPlans = new ArrayList<>(this.treatmentPlans);
// Note: Immutable fields (String patientId, String name) are safely shared
// Note: InsurancePlan reference sharing is acceptable for this use case
return clonedRecord;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new AssertionError(); // Should never happen
}
}
Constructor vs Clone Performance Analysis
// Traditional constructor approach
PatientRecord newPatient = new PatientRecord("P002", "John Doe");
newPatient.setMedicalHistory(existingHistory);
newPatient.setTreatmentPlans(existingPlans);
newPatient.setInsurancePlan(existingPlan);
// Prototype pattern approach
PatientRecord templatePatient = /* existing patient with baseline data */;
PatientRecord newPatient = templatePatient.clone();
newPatient.setPatientId("P002"); // Only change what's different
newPatient.setName("John Doe");
5. Pattern Integration
5.1 Controller Integration
public class PatientController {
private PatientRecord currentPatient;
private RecordHistory recordHistory; // Memento caretaker
private void searchPatient() {
currentPatient = dao.getPatientById(patientId);
if (currentPatient != null) {
// Initialize memento system for undo functionality
recordHistory = new RecordHistory(currentPatient);
displayPatientData();
}
}
private void editPatient() {
// Save current state before allowing edits
recordHistory.save();
view.setFieldsEditable(true);
}
private void undoChanges() {
if (recordHistory != null) {
recordHistory.undo(); // Restore from memento
displayPatientData(); // Update UI with restored state
}
}
}
5.2 Workflow Integration
User Workflow:
1. Search Patient → Load existing record → Create RecordHistory
2. Edit Patient → Save current state to memento → Enable editing
3. Make Changes → Modify patient record state
4. Undo (Optional) → Restore from memento → Update UI
5. Save Changes → Persist to database → Clear undo history
6. Usage Scenarios
6.1 Scenario 1: Medical Record Editing with Undo
// 1. User loads patient record
PatientRecord patient = dao.getPatientById("P001");
RecordHistory history = new RecordHistory(patient);
// 2. User starts editing - save current state
history.save();
patient.setName("Updated Name");
patient.addMedicalHistory("New diagnosis: Hypertension");
// 3. User realizes mistake and wants to undo
history.undo(); // Restores to state before editing
// 4. Patient record is back to original state
assert patient.getName().equals("Original Name");
6.2 Scenario 2: Creating Patient Templates
// 1. Create a baseline patient template
PatientRecord template = new PatientRecord("TEMPLATE", "Template Patient");
template.addMedicalHistory("Standard health screening completed");
template.addTreatmentPlan("Annual checkup recommended");
template.setInsurancePlan(standardInsurancePlan);
// 2. Use template to create new patients efficiently
PatientRecord newPatient1 = template.clone();
newPatient1.setPatientId("P003");
newPatient1.setName("Alice Johnson");
PatientRecord newPatient2 = template.clone();
newPatient2.setPatientId("P004");
newPatient2.setName("Bob Smith");
6.3 Scenario 3: Complex Editing Session
RecordHistory history = new RecordHistory(patient);
// Multiple edit points with saves
history.save(); // Save point 1
patient.addMedicalHistory("Initial consultation");
history.save(); // Save point 2
patient.addTreatmentPlan("Medication prescribed");
history.save(); // Save point 3
patient.addMedicalHistory("Follow-up scheduled");
// User wants to undo back to save point 2
history.undo(); // Removes follow-up
history.undo(); // Removes treatment plan
// Now at save point 1 with only initial consultation
7. Benefits & Trade-offs
7.1 Memento Pattern Benefits
Encapsulation Preservation
- Internal state never exposed to external classes
- Package-private access ensures controlled state access
- Memento is opaque to caretaker (RecordHistory)
Undo/Redo Capability
- Clean undo functionality without complex state tracking
- Multiple save points supported through stack structure
- Atomic state restoration guarantees consistency
Flexibility
- Easy to extend to support redo functionality
- Can implement selective state restoration
- Supports branching undo scenarios
7.2 Prototype Pattern Benefits
Performance Optimization
- Avoids expensive object initialization
- Reduces constructor complexity for template objects
- Efficient for objects with complex default state
Flexibility in Object Creation
- Runtime determination of object types to create
- Easy template management and versioning
- Supports object creation without knowing concrete classes
7.3 Trade-offs and Considerations
Memory Usage
- Memento pattern: Each save point consumes memory
- Deep copying in both patterns increases memory footprint
- Stack growth in RecordHistory needs monitoring
Complexity
- Additional classes and relationships to maintain
- Deep vs shallow copying decisions need careful consideration
- Synchronization concerns in multi-threaded environments
Performance
- Clone operation has O(n) complexity for collections
- Memento creation and restoration overhead
- Stack operations add computational cost
8. Testing & Validation
8.1 Memento Pattern Test Cases
@Test
public void testMementoBasicSaveRestore() {
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "John Doe");
RecordHistory history = new RecordHistory(patient);
// Save initial state
history.save();
// Modify state
patient.setName("Jane Doe");
patient.addMedicalHistory("Diagnosis added");
// Verify changes
assertEquals("Jane Doe", patient.getName());
assertEquals(1, patient.getMedicalHistoryList().size());
// Restore and verify
history.undo();
assertEquals("John Doe", patient.getName());
assertEquals(0, patient.getMedicalHistoryList().size());
}
@Test
public void testMementoEncapsulation() {
PatientRecord patient = new PatientRecord("P001", "John Doe");
PatientRecordMemento memento = patient.save();
// Verify memento returns defensive copies
List<String> history1 = memento.getMedicalHistory();
List<String> history2 = memento.getMedicalHistory();
assertNotSame(history1, history2); // Different instances
assertEquals(history1, history2); // Same content
}
8.2 Prototype Pattern Test Cases
@Test
public void testPrototypeDeepCloning() {
PatientRecord original = new PatientRecord("P001", "John Doe");
original.addMedicalHistory("Original history");
PatientRecord clone = original.clone();
// Verify independence
clone.addMedicalHistory("Clone history");
assertEquals(1, original.getMedicalHistoryList().size());
assertEquals(2, clone.getMedicalHistoryList().size());
}
@Test
public void testPrototypeSharedImmutableData() {
PatientRecord original = new PatientRecord("P001", "John Doe");
PatientRecord clone = original.clone();
// Immutable strings can be safely shared
assertSame(original.getPatientId(), clone.getPatientId());
assertSame(original.getName(), clone.getName());
}
8.3 Integration Test Scenarios
@Test
public void testMementoWithPrototype() {
// Create template
PatientRecord template = new PatientRecord("TEMPLATE", "Template");
template.addMedicalHistory("Standard screening");
// Clone template
PatientRecord patient = template.clone();
patient.setPatientId("P001");
patient.setName("John Doe");
// Test memento on cloned object
RecordHistory history = new RecordHistory(patient);
history.save();
patient.addMedicalHistory("New diagnosis");
history.undo();
// Should restore to post-clone state
assertEquals("John Doe", patient.getName());
assertEquals(1, patient.getMedicalHistoryList().size());
assertEquals("Standard screening", patient.getMedicalHistoryList().get(0));
}
8.4 UI Integration Validation
User Workflow Testing
- Load patient record → Verify RecordHistory initialization
- Click "Edit" → Verify memento save operation
- Modify data → Verify UI updates
- Click "Undo" → Verify state restoration and UI refresh
- Verify database consistency after operations
Performance Testing
- Measure memento creation time for records with large medical histories
- Test memory usage with multiple save points
- Validate clone operation performance with complex patient records
Conclusion
The implementation of Memento and Prototype patterns in the patient record management system demonstrates a sophisticated approach to state management and object creation in healthcare software. The patterns work together to provide:
- Robust Undo Functionality: Critical for healthcare data integrity
- Efficient Record Creation: Important for busy healthcare environments
- Proper Encapsulation: Essential for sensitive medical data
- Scalable Architecture: Supports complex healthcare workflows
The dual-pattern approach addresses real-world healthcare domain challenges while maintaining clean, maintainable code that follows established design principles.
Document Status: Part A Complete
Next: Part B - Appointment Scheduling (Mediator Pattern)