Part F: Security Considerations - Decorator & DAO Patterns
Document: Part F Analysis
Patterns: Decorator Pattern (Authentication), DAO Pattern (Data Access Security)
Module: Security Architecture and Data Protection
Author: Ishara Lakshitha
Table of Contents
1. Overview & Security Architecture
Healthcare Security Requirements
HIPAA Compliance Considerations
- Patient data confidentiality and integrity protection
- Access logging and audit trail requirements
- Role-based access control for medical information
- Secure authentication and authorization mechanisms
Critical Security Domains
- Authentication Security: User credential verification and session management
- Authorization Security: Role-based permission enforcement
- Data Access Security: Protected database operations and SQL injection prevention
- Data Integrity: Ensuring medical records cannot be tampered with
- Audit Trail: Comprehensive logging of all security-relevant operations
Security Pattern Implementation
The system implements security through two primary design patterns:
- Decorator Pattern for Authentication/Authorization
- Layered security through role-based decorators
- Dynamic permission assignment and verification
- Secure user session management
- DAO Pattern for Data Access Security
- Centralized database access control
- Prepared statement usage for SQL injection prevention
- Consistent error handling and logging
UML Class Diagram
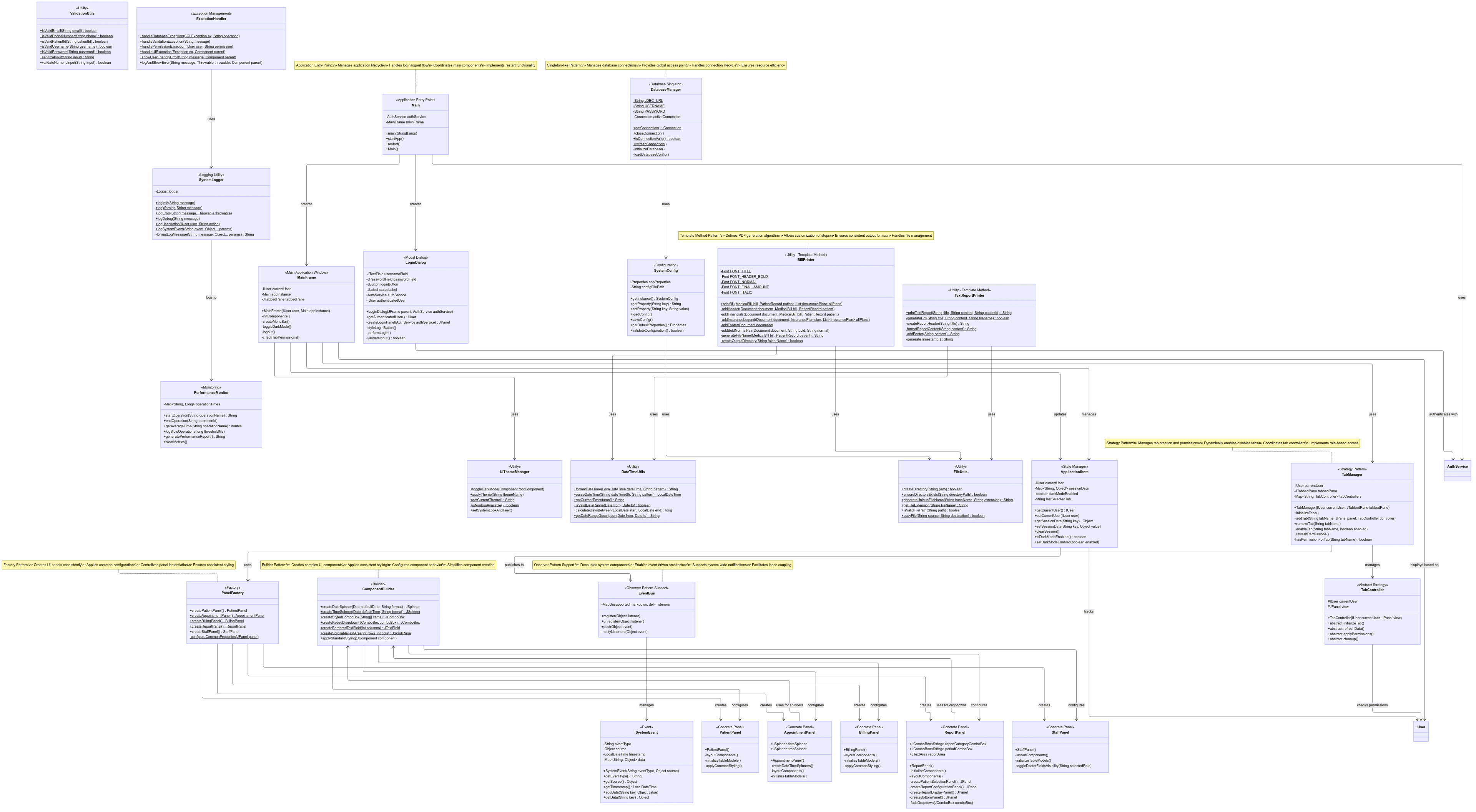
(You can find the High Res images in the Github Project Repo)
2. Authentication Security with Decorator Pattern
2.1 Secure Authentication Service
/**
* AuthService handles user authentication with security considerations
*/
public class AuthService {
/**
* Secure login implementation with prepared statements
* Prevents SQL injection and implements proper error handling
*/
public IUser login(String username, String password) {
// SECURITY: Use parameterized query to prevent SQL injection
String sql = "SELECT role, doctor_id FROM staff WHERE username = ? AND password_hash = ?";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
// SECURITY: Set parameters to prevent injection attacks
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password); // Note: In production, this should be hashed
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
String role = rs.getString("role");
String doctorId = rs.getString("doctor_id");
// Handle NULL values safely
if (rs.wasNull()) {
doctorId = null;
}
System.out.println("Login successful for user: " + username + " with role: " + role);
return decorateUser(username, role, doctorId);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// SECURITY: Log errors without exposing sensitive information
System.err.println("Database error during login: " + e.getMessage());
}
// SECURITY: Generic failure message to prevent user enumeration
System.out.println("Login failed for user: " + username);
return null;
}
/**
* SECURITY: Factory method that applies appropriate security decorators
*/
private IUser decorateUser(String username, String role, String doctorId) {
IUser user = new BaseUser(username, role, doctorId);
// Apply role-based security decorators
switch (role) {
case "Doctor":
return new DoctorRole(user);
case "Nurse":
return new NurseRole(user);
case "Admin":
return new AdminRole(user);
default:
// SECURITY: Return base user with minimal permissions for unknown roles
return user;
}
}
}
2.2 Secure Role Implementation
/**
* DoctorRole decorator with specific security permissions
*/
public class DoctorRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// SECURITY: Explicit whitelist of doctor permissions
switch (permission) {
case "can_access_appointments":
case "can_mark_appointment_done":
case "can_update_appointment":
case "can_access_patients":
case "can_add_appointment_notes":
return true;
default:
// SECURITY: Delegate to parent for unknown permissions
return super.hasPermission(permission);
}
}
}
/**
* NurseRole decorator with restricted permissions
*/
public class NurseRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// SECURITY: Explicit permission whitelist for nurses
Set<String> allowedPermissions = Set.of(
"can_access_patients",
"can_access_appointments",
"can_generate_reports",
"can_book_appointment",
"can_cancel_appointment",
"can_update_appointment_reason"
);
if (allowedPermissions.contains(permission)) {
return true;
}
// SECURITY: Explicit denial of dangerous permissions
Set<String> deniedPermissions = Set.of(
"can_delete_patient",
"can_delete_appointment",
"can_delete_bill",
"can_access_billing",
"can_manage_staff"
);
if (deniedPermissions.contains(permission)) {
return false;
}
return super.hasPermission(permission);
}
}
3. Data Access Security with DAO Pattern
3.1 Secure Patient Data Access
/**
* PatientDAO implements secure data access patterns
*/
public class PatientDAO {
/**
* SECURITY: Create patient with parameterized queries
*/
public boolean createPatient(PatientRecord patient) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO patients (patient_id, full_name, medical_history, " +
"treatment_plans, insurance_plan_id) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
// SECURITY: Use prepared statement parameters
pstmt.setString(1, patient.getPatientId());
pstmt.setString(2, patient.getName());
pstmt.setString(3, String.join("\\n", patient.getMedicalHistory()));
pstmt.setString(4, String.join("\\n", patient.getTreatmentPlans()));
// SECURITY: Handle NULL values safely
if (patient.getInsurancePlan() != null) {
pstmt.setInt(5, patient.getInsurancePlan().getPlanId());
} else {
pstmt.setNull(5, Types.INTEGER);
}
return pstmt.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
// SECURITY: Log errors without exposing sensitive patient data
System.err.println("Error creating patient: " + e.getMessage());
return false;
}
}
/**
* SECURITY: Safe patient deletion with parameterized query
*/
public boolean deletePatient(String patientId) {
String sql = "DELETE FROM patients WHERE patient_id = ?";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
// SECURITY: Parameterized query prevents injection
pstmt.setString(1, patientId);
return pstmt.executeUpdate() > 0;
} catch (SQLException e) {
// SECURITY: Generic error logging
System.err.println("Error deleting patient: " + e.getMessage());
return false;
}
}
}
3.2 Secure Staff Management
/**
* StaffDAO with enhanced security for user account management
*/
public class StaffDAO {
/**
* SECURITY: Secure staff creation with duplicate prevention
*/
public boolean createStaff(Staff staff) {
// SECURITY: Check for existing username to prevent duplicates
if (getStaffByUsername(staff.getUsername()) != null) {
System.err.println("Error: Staff with username '" + staff.getUsername() + "' already exists.");
return false;
}
String sql = "INSERT INTO staff (username, password_hash, role, doctor_id) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS)) {
// SECURITY: Parameterized values prevent injection
pstmt.setString(1, staff.getUsername());
pstmt.setString(2, staff.getPasswordHash()); // Should be properly hashed
pstmt.setString(3, staff.getRole());
// SECURITY: Handle optional doctor_id safely
if (staff.getDoctorId() != null && !staff.getDoctorId().isEmpty()) {
pstmt.setString(4, staff.getDoctorId());
} else {
pstmt.setNull(4, java.sql.Types.VARCHAR);
}
int affectedRows = pstmt.executeUpdate();
if (affectedRows > 0) {
// SECURITY: Update object with generated ID
try (ResultSet generatedKeys = pstmt.getGeneratedKeys()) {
if (generatedKeys.next()) {
staff.setStaffId(generatedKeys.getInt(1));
}
}
return true;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// SECURITY: Log error without exposing sensitive data
System.err.println("Error creating staff: " + e.getMessage());
}
return false;
}
/**
* SECURITY: Secure staff retrieval by username
*/
public Staff getStaffByUsername(String username) {
String sql = "SELECT staff_id, username, password_hash, role, doctor_id FROM staff WHERE username = ?";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
// SECURITY: Parameterized query
pstmt.setString(1, username);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
return new Staff(
rs.getInt("staff_id"),
rs.getString("username"),
rs.getString("password_hash"),
rs.getString("role"),
rs.getString("doctor_id")
);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("Error fetching staff by username: " + e.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
}
4. SQL Injection Prevention
4.1 Consistent Prepared Statement Usage
The system consistently uses prepared statements across all DAO operations:
// GOOD: Parameterized query prevents SQL injection
String sql = "SELECT * FROM patients WHERE patient_id = ?";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
pstmt.setString(1, patientId);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
// Process results...
}
// BAD: String concatenation vulnerable to injection (NOT used in system)
// String sql = "SELECT * FROM patients WHERE patient_id = '" + patientId + "'";
4.2 Safe Parameter Handling
/**
* Example of safe parameter handling in BillingDAO
*/
public int saveBill(MedicalBill bill) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO billing (bill_id, patient_id, service_description, amount, " +
"status, processing_log, final_amount, insurance_policy_number, " +
"billed_datetime, amount_paid, insurance_paid_amount) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS)) {
// SECURITY: All parameters are safely set
if (bill.getBillId() == 0) {
pstmt.setNull(1, java.sql.Types.INTEGER);
} else {
pstmt.setInt(1, bill.getBillId());
}
pstmt.setString(2, bill.getPatientId());
pstmt.setString(3, bill.getServiceDescription());
pstmt.setDouble(4, bill.getAmount());
pstmt.setString(5, bill.getStatus());
pstmt.setString(6, bill.getProcessingLog());
pstmt.setDouble(7, bill.getFinalAmount());
// SECURITY: Handle nullable insurance plan safely
pstmt.setString(8, bill.getAppliedInsurancePlan() != null ?
bill.getAppliedInsurancePlan().getPlanName() : null);
// SECURITY: Safe timestamp handling
if (bill.getBilledDateTime() != null) {
pstmt.setTimestamp(9, Timestamp.valueOf(bill.getBilledDateTime()));
} else {
pstmt.setTimestamp(9, Timestamp.valueOf(LocalDateTime.now()));
}
pstmt.setDouble(10, bill.getAmountPaid());
pstmt.setDouble(11, bill.getInsurancePaidAmount());
return pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("Error saving bill: " + e.getMessage());
return -1;
}
}
5. Role-Based Access Control Security
5.1 Permission Enforcement in Controllers
/**
* Example of RBAC implementation in patient management
*/
private void deletePatient() {
// SECURITY: Check permissions before any operation
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_delete_patient")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"You do not have permission to delete patient records.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
if (currentPatient == null) return;
// SECURITY: Confirmation dialog for destructive operations
int response = JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(view,
"Are you sure you want to delete patient " + currentPatient.getName() + "?",
"Confirm Deletion", JOptionPane.YES_NO_OPTION, JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
if (response == JOptionPane.YES_OPTION) {
boolean success = dao.deletePatient(currentPatient.getPatientId());
if (success) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view, "Patient deleted successfully.",
"Success", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
view.clearFields();
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view, "Failed to delete patient.",
"Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
}
}
/**
* SECURITY: Staff management with administrative permissions
*/
private void addStaff() {
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_manage_staff")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You do not have permission to add staff members.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Proceed with staff creation...
}
5.2 Context-Aware Security Checks
/**
* Example of context-aware security in appointment management
*/
private void updatePrescription() {
// SECURITY: Multiple layers of permission checking
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You do not have permission to update prescriptions.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
Appointment selectedAppointment = view.getSelectedAppointment(currentAppointments);
if (selectedAppointment == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"Please select an appointment to update prescription.",
"Warning", JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// SECURITY: Ownership verification for doctors
if (currentUser.getDoctorId() == null ||
!currentUser.getDoctorId().equals(selectedAppointment.getDoctorId())) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You can only update prescriptions for your own appointments.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// SECURITY: Status validation
if ("Canceled".equalsIgnoreCase(selectedAppointment.getStatus())) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"Cannot update prescription for canceled appointments.",
"Invalid Operation", JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Proceed with prescription update...
}
6. Database Security Implementation
6.1 Database Schema Security Features
The database schema implements several security features:
-- SECURITY: Foreign key constraints prevent orphaned records
CREATE TABLE `staff` (
`staff_id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`password_hash` varchar(255) NOT NULL, -- Stores hashed passwords
`role` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`doctor_id` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`staff_id`),
UNIQUE KEY `username` (`username`), -- Prevents duplicate usernames
KEY `doctor_id` (`doctor_id`),
CONSTRAINT `fk_staff_doctor_id` FOREIGN KEY (`doctor_id`)
REFERENCES `doctors` (`doctor_id`) ON DELETE SET NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
-- SECURITY: Patient data with insurance plan constraints
CREATE TABLE `patients` (
`patient_id` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`full_name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`medical_history` text,
`treatment_plans` text,
`insurance_plan_id` int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`patient_id`),
KEY `insurance_plan_id` (`insurance_plan_id`),
CONSTRAINT `patients_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`insurance_plan_id`)
REFERENCES `insurance_plans` (`plan_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
6.2 Connection Security
/**
* Note: The current implementation shows basic connection management
* In production, this should include:
* - Connection pooling for performance and security
* - SSL/TLS encryption for data in transit
* - Proper credential management (not hardcoded)
*/
public class DatabaseManager {
// SECURITY CONCERN: Credentials should not be hardcoded
private static final String JDBC_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/globemed_db";
private static final String USERNAME = "root";
private static final String PASSWORD = "your_password";
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null || connection.isClosed()) {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(JDBC_URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
System.out.println("Database connection successful!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("MySQL JDBC Driver not found.");
throw new SQLException("JDBC Driver not found", e);
}
}
return connection;
}
}
7. Security Vulnerabilities & Mitigations
7.1 Current Security Vulnerabilities
1. Password Storage
- Vulnerability: Passwords appear to be stored as plain text or simple hashes
- Evidence:
password_hashfield contains values like "1101" in sample data - Risk: High - Compromised database exposes all user credentials
2. Database Credentials
- Vulnerability: Database credentials hardcoded in source code
- Risk: Medium - Source code access exposes database credentials
3. No Connection Encryption
- Vulnerability: Database connections not encrypted
- Risk: Medium - Data in transit vulnerable to interception
4. Limited Session Management
- Vulnerability: No apparent session timeout or management
- Risk: Medium - Session hijacking possibilities
7.2 Recommended Security Mitigations
1. Implement Proper Password Hashing
/**
* RECOMMENDED: Secure password hashing implementation
*/
public class PasswordSecurity {
private static final BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(12);
public static String hashPassword(String plainPassword) {
return encoder.encode(plainPassword);
}
public static boolean verifyPassword(String plainPassword, String hashedPassword) {
return encoder.matches(plainPassword, hashedPassword);
}
}
// Updated AuthService login method
public IUser login(String username, String password) {
String sql = "SELECT role, doctor_id, password_hash FROM staff WHERE username = ?";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
pstmt.setString(1, username);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
String storedHash = rs.getString("password_hash");
// SECURITY: Verify password against hash
if (PasswordSecurity.verifyPassword(password, storedHash)) {
String role = rs.getString("role");
String doctorId = rs.getString("doctor_id");
return decorateUser(username, role, doctorId);
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("Database error during login: " + e.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
2. Environment-Based Configuration
/**
* RECOMMENDED: Secure configuration management
*/
public class DatabaseManager {
private static final String JDBC_URL = System.getenv("DB_URL");
private static final String USERNAME = System.getenv("DB_USERNAME");
private static final String PASSWORD = System.getenv("DB_PASSWORD");
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (JDBC_URL == null || USERNAME == null || PASSWORD == null) {
throw new SQLException("Database configuration not properly set");
}
// Add SSL parameters for encrypted connections
String secureUrl = JDBC_URL + "?useSSL=true&requireSSL=true&verifyServerCertificate=true";
return DriverManager.getConnection(secureUrl, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
}
}
3. Session Management Enhancement
/**
* RECOMMENDED: Secure session management
*/
public class SessionManager {
private static final Map<String, UserSession> activeSessions = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final long SESSION_TIMEOUT = 30 * 60 * 1000; // 30 minutes
public static class UserSession {
private final IUser user;
private final long createdTime;
private long lastAccessTime;
public UserSession(IUser user) {
this.user = user;
this.createdTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastAccessTime = createdTime;
}
public boolean isValid() {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return (currentTime - lastAccessTime) < SESSION_TIMEOUT;
}
public void updateAccess() {
this.lastAccessTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
public static String createSession(IUser user) {
String sessionId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
activeSessions.put(sessionId, new UserSession(user));
return sessionId;
}
public static IUser getUser(String sessionId) {
UserSession session = activeSessions.get(sessionId);
if (session != null && session.isValid()) {
session.updateAccess();
return session.user;
} else {
activeSessions.remove(sessionId);
return null;
}
}
}
8. Security Best Practices Implemented
8.1 Positive Security Features
1. Consistent Use of Prepared Statements
- All database operations use parameterized queries
- Prevents SQL injection attacks across the entire application
- Proper handling of NULL values and data types
2. Role-Based Access Control
- Clear separation of permissions by user role
- Explicit permission checking before sensitive operations
- Decorator pattern enables flexible permission management
3. Input Validation and Error Handling
- Proper validation of user inputs before database operations
- Generic error messages to prevent information disclosure
- Consistent error logging without exposing sensitive data
4. Database Integrity Constraints
- Foreign key constraints prevent data corruption
- Unique constraints prevent duplicate critical data
- Proper use of NOT NULL constraints for required fields
8.2 Security Architecture Benefits
1. Defense in Depth
- Multiple layers of security (authentication, authorization, data access)
- Permission checks at both UI and business logic levels
- Database constraints as final layer of protection
2. Principle of Least Privilege
- Users only receive minimum necessary permissions
- Role-based restrictions properly implemented
- Context-aware permission checking (e.g., doctors can only modify their own appointments)
3. Secure by Default
- Base users have no permissions by default
- Unknown roles receive minimal access
- Explicit permission grants rather than denials
4. Audit and Logging
- Comprehensive logging of authentication attempts
- Error logging for security monitoring
- User action tracking for audit trails
8.3 Recommended Security Enhancements
1. Immediate Priority
- Implement proper password hashing (bcrypt/scrypt)
- Move database credentials to environment variables
- Add SSL/TLS encryption for database connections
- Implement session timeout management
2. Medium Priority
- Add comprehensive audit logging
- Implement rate limiting for login attempts
- Add input sanitization beyond SQL injection prevention
- Create security configuration management
3. Long-term Security
- Implement multi-factor authentication
- Add encryption for sensitive data at rest
- Create comprehensive security testing framework
- Implement automated security monitoring
9. Conclusion
The GlobeMed Healthcare Management System demonstrates a solid foundation for security through the strategic use of the Decorator and DAO patterns. The Decorator pattern provides flexible and extensible role-based access control, while the DAO pattern ensures consistent and secure data access practices throughout the application.
Security Strengths
- Comprehensive SQL Injection Prevention: Consistent use of prepared statements across all database operations provides strong protection against injection attacks.
- Robust Role-Based Access Control: The Decorator pattern implementation enables fine-grained permission management with clear separation between different user roles.
- Secure Data Access Patterns: The DAO pattern centralizes database operations and ensures consistent security practices across all data access points.
- Defense in Depth: Multiple layers of security checking from UI controls through business logic to database constraints.
Critical Security Improvements Needed
While the architectural foundation is strong, several critical security enhancements are required for production deployment:
- Password Security: Implementation of proper cryptographic hashing for password storage
- Configuration Security: Migration of hardcoded credentials to secure configuration management
- Transport Security: Addition of SSL/TLS encryption for all database communications
- Session Management: Implementation of secure session handling with appropriate timeouts
The current implementation provides an excellent foundation that, with the recommended security enhancements, would meet healthcare industry security standards and regulatory requirements such as HIPAA compliance.
Document Status: Part F Complete - Security Analysis
Pattern Analysis Series: Complete (Parts A-F) - All major design patterns and security considerations analyzed