Part D: Medical Staff Roles and Permissions - Decorator Pattern
Document: Part D Analysis
Pattern: Decorator Pattern
Module: Medical Staff Roles and Permissions System
Author: Ishara Lakshitha
Table of Contents
1. Overview & Problem Statement
Healthcare Domain Problems Addressed
Problem 1: Complex Role-Based Access Control
- Healthcare systems require sophisticated permission management
- Different medical staff roles have distinct access privileges
- Permissions must be granular for patient safety and regulatory compliance
- Need flexible system to add new roles or modify existing permissions
Problem 2: Hierarchical Permission Structure
- Medical staff roles have overlapping but distinct responsibilities
- Doctors can perform medical procedures but have limited administrative access
- Nurses have patient care permissions but cannot perform certain medical functions
- Administrators have system-wide access but limited clinical permissions
Problem 3: Dynamic Permission Assignment
- Staff members may have multiple roles or temporary elevated permissions
- Need to combine permissions from different roles dynamically
- Must maintain audit trail of permission usage
- System should support role delegation and temporary access
Solution Approach
The Decorator Pattern provides a flexible permission system where:
- BaseUser serves as the core component with minimal permissions
- Role Decorators (DoctorRole, NurseRole, AdminRole) add specific permissions
- Dynamic Composition allows combining multiple roles if needed
- Extensible Architecture supports adding new roles without modifying existing code
2. Decorator Pattern Implementation
2.1 Pattern Participants
Component Interface
/**
* The Component interface for the Decorator pattern.
* Defines the operations that can be altered by decorators.
*/
public interface IUser {
String getUsername();
String getRole();
String getDoctorId();
boolean hasPermission(String permission);
}
Concrete Component
/**
* The Concrete Component. A base user object that represents a
* logged-in user with basic information but no special permissions.
*/
public class BaseUser implements IUser {
private final String username;
private final String role;
private final String doctorId;
public BaseUser(String username, String role, String doctorId) {
this.username = username;
this.role = role;
this.doctorId = doctorId;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() { return this.username; }
@Override
public String getRole() { return this.role; }
@Override
public String getDoctorId() { return this.doctorId; }
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
return false; // Base user has no permissions
}
}
Abstract Decorator
/**
* The abstract Decorator class. It holds a reference to a component object
* and delegates all requests to it. Its main purpose is to define a
* wrapping interface for all concrete decorators.
*/
public abstract class UserRoleDecorator implements IUser {
protected final IUser wrappedUser;
public UserRoleDecorator(IUser user) {
this.wrappedUser = user;
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return wrappedUser.getUsername();
}
@Override
public String getRole() {
return wrappedUser.getRole();
}
@Override
public String getDoctorId() {
return wrappedUser.getDoctorId();
}
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// Delegate to the wrapped user by default.
// Concrete decorators will override this.
return wrappedUser.hasPermission(permission);
}
}
Concrete Decorator 1: DoctorRole
/**
* Decorator that adds doctor-specific permissions
*/
public class DoctorRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
public DoctorRole(IUser user) {
super(user);
}
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// Doctor-specific permissions
if ("can_access_appointments".equals(permission) ||
"can_mark_appointment_done".equals(permission) ||
"can_update_appointment".equals(permission) ||
"can_access_patients".equals(permission) ||
"can_add_appointment_notes".equals(permission)) {
return true;
}
// Delegate to wrapped user for other permissions
return super.hasPermission(permission);
}
}
Concrete Decorator 2: NurseRole
/**
* Decorator that adds nurse-specific permissions
*/
public class NurseRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
public NurseRole(IUser user) {
super(user);
}
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// Nurse-specific permissions
if ("can_access_patients".equals(permission) ||
"can_access_appointments".equals(permission) ||
"can_generate_reports".equals(permission) ||
"can_book_appointment".equals(permission) ||
"can_cancel_appointment".equals(permission) ||
"can_update_appointment_reason".equals(permission)) {
return true;
}
// Nurses explicitly DO NOT have these permissions:
// "can_delete_patient", "can_delete_appointment", "can_delete_bill",
// "can_mark_appointment_done", "can_access_billing", "can_view_all_patients"
return super.hasPermission(permission);
}
}
Concrete Decorator 3: AdminRole
/**
* Decorator that grants administrative permissions
*/
public class AdminRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
public AdminRole(IUser user) {
super(user);
}
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// Admins have all permissions
return true;
}
}
2.2 Factory Method for User Decoration
/**
* AuthService handles user authentication and role decoration
*/
public class AuthService {
public IUser login(String username, String password) {
// Database authentication logic
String sql = "SELECT role, doctor_id FROM staff WHERE username = ? AND password_hash = ?";
try (Connection conn = DatabaseManager.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
String role = rs.getString("role");
String doctorId = rs.getString("doctor_id");
if (rs.wasNull()) {
doctorId = null;
}
System.out.println("Login successful for user: " + username +
" with role: " + role +
(doctorId != null ? " (Doctor ID: " + doctorId + ")" : ""));
return decorateUser(username, role, doctorId);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.err.println("Database error during login: " + e.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
/**
* Factory method to construct the appropriate decorated user object.
*/
private IUser decorateUser(String username, String role, String doctorId) {
// Create base user
IUser user = new BaseUser(username, role, doctorId);
// Apply role-specific decorator
switch (role) {
case "Doctor":
return new DoctorRole(user);
case "Nurse":
return new NurseRole(user);
case "Admin":
return new AdminRole(user);
default:
return user; // Return base user with no additional permissions
}
}
}
3. UML Class Diagrams
3.0 Comprehensive Diagram
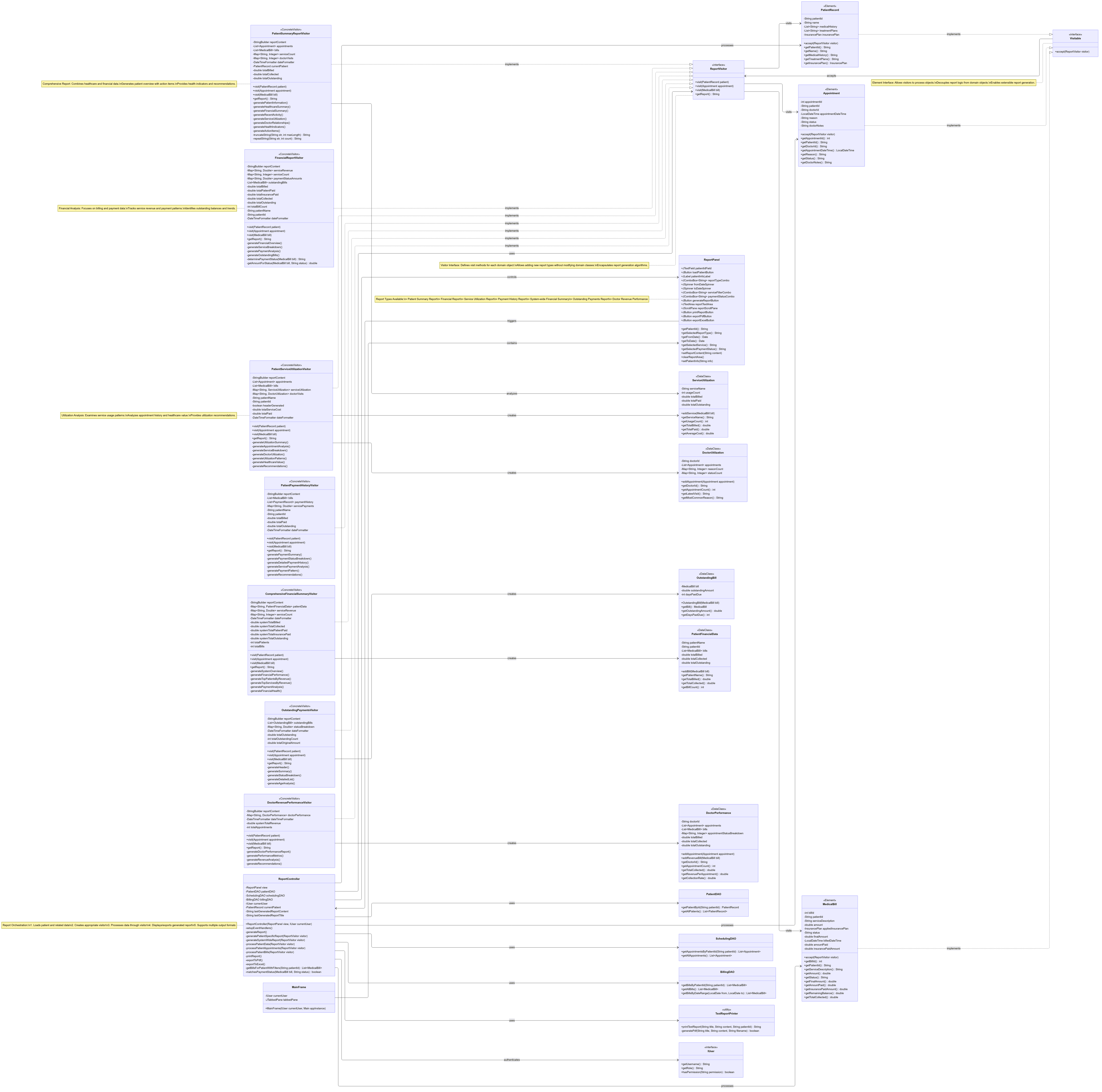
(You can find the High Res images in the Github Project Repo)
3.1 Decorator Pattern Structure
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ <<interface>> │
│ IUser │
├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│ + getUsername(): String │
│ + getRole(): String │
│ + getDoctorId(): String │
│ + hasPermission(permission): boolean│
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
▲
┌───────────┼───────────┐
│ │ │
┌───────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ BaseUser │ │ UserRoleDecorator │
│ (Component) │ │ (Abstract Decorator) │
├───────────────┤ ├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│- username │ │# wrappedUser: IUser │
│- role │ ├─────────────────────────────────────┤
│- doctorId │ │+ getUsername(): String │
├───────────────┤ │+ getRole(): String │
│+ getUsername()│ │+ getDoctorId(): String │
│+ getRole() │ │+ hasPermission(permission): boolean │
│+ getDoctorId()│ └─────────────────────────────────────┘
│+ hasPermission│ ▲
│ (): boolean │ ┌─────────┼─────────┐
└───────────────┘ │ │ │
┌───────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐
│DoctorRole │ │NurseRole│ │AdminRole│
│(Concrete │ │(Concrete│ │(Concrete│
│Decorator) │ │Decorator│ │Decorator│
├───────────┤ ├─────────┤ ├─────────┤
│+ has │ │+ has │ │+ has │
│Permission │ │Permission│ │Permission│
│(): boolean│ │(): bool │ │(): bool │
└───────────┘ └─────────┘ └─────────┘
3.2 Permission Flow Diagram
Client Request → Controller → IUser.hasPermission() → Decorator Chain
Example: Doctor updating appointment notes
AppointmentController.updatePrescription()
│
▼
currentUser.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes")
│
▼
DoctorRole.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes")
│
├─→ "can_add_appointment_notes" found in doctor permissions
│ │
│ ▼
│ return true
│
└─→ (if not found) super.hasPermission(permission)
│
▼
BaseUser.hasPermission() → return false
4. Detailed Code Analysis
4.1 Permission Grant Matrix
| Permission | Doctor | Nurse | Admin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
can_access_patients | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | View patient records |
can_access_appointments | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | View appointment schedules |
can_book_appointment | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | Schedule new appointments |
can_cancel_appointment | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | Cancel existing appointments |
can_update_appointment_reason | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | Modify appointment reasons |
can_mark_appointment_done | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | Mark appointments as completed |
can_add_appointment_notes | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | Add/edit medical notes |
can_delete_patient | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | Remove patient records |
can_delete_appointment | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | Permanently delete appointments |
can_manage_doctors | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | CRUD operations on doctor records |
can_manage_staff | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | CRUD operations on staff records |
can_access_billing | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | Access billing information |
can_process_payments | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | Process patient payments |
can_generate_reports | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | Generate system reports |
4.2 Controller Integration Examples
Patient Controller Permission Usage
public class PatientController {
private final IUser currentUser;
private void initController() {
// View all patients permission check
view.viewAllButton.setEnabled(currentUser.hasPermission("can_view_all_patients"));
}
private void deletePatient() {
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_delete_patient")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"You do not have permission to delete patient records.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Proceed with deletion logic
}
}
Appointment Controller Permission Usage
public class AppointmentController {
private void applyPermissions() {
// Doctor-specific access based on doctor ID
view.viewScheduleButton.setEnabled(
currentUser.getDoctorId() != null ||
(view.doctorsTable.getSelectedRow() != -1 &&
currentUser.hasPermission("can_access_appointments"))
);
// General appointment permissions
view.viewAllAppointmentsButton.setEnabled(
currentUser.hasPermission("can_access_appointments")
);
view.bookAppointmentButton.setEnabled(
currentUser.hasPermission("can_book_appointment")
);
// Administrative permissions
boolean canManageDoctors = currentUser.hasPermission("can_manage_doctors");
view.setDoctorCrudFieldsEditable(canManageDoctors);
view.addDoctorButton.setEnabled(canManageDoctors);
}
private void updateButtonStatesBasedOnSelection() {
Appointment selectedAppt = view.getSelectedAppointment(currentAppointments);
if (selectedAppt == null) return;
String status = selectedAppt.getStatus();
boolean isOwner = currentUser.getDoctorId() != null &&
currentUser.getDoctorId().equals(selectedAppt.getDoctorId());
boolean isDoctor = currentUser.getDoctorId() != null;
boolean isNurseOrAdmin = !isDoctor;
// Nurse/Admin can update appointment reasons for scheduled appointments
boolean canUpdateReason = currentUser.hasPermission("can_update_appointment_reason") &&
isNurseOrAdmin &&
"Scheduled".equalsIgnoreCase(status);
view.updateAppointmentButton.setEnabled(canUpdateReason);
// Doctors can add notes to their own appointments
boolean canUpdatePrescription = currentUser.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes") &&
isOwner && isDoctor &&
!"Canceled".equalsIgnoreCase(status);
view.updatePrescriptionButton.setEnabled(canUpdatePrescription);
// Cancel permissions based on role and ownership
boolean canCancel = currentUser.hasPermission("can_cancel_appointment") &&
!"Done".equalsIgnoreCase(status) &&
!"Canceled".equalsIgnoreCase(status) &&
(isOwner || isNurseOrAdmin);
view.cancelAppointmentButton.setEnabled(canCancel);
}
}
Staff Controller Permission Usage
public class StaffController {
private void applyPermissions() {
boolean canManageStaff = currentUser.hasPermission("can_manage_staff");
boolean isStaffSelected = view.staffTable.getSelectedRow() != -1;
// Enable/disable form fields based on permissions
view.setFormEditable(canManageStaff);
view.refreshStaffButton.setEnabled(canManageStaff);
// CRUD button permissions
view.addButton.setEnabled(canManageStaff && !isStaffSelected);
view.updateButton.setEnabled(canManageStaff && isStaffSelected);
view.deleteButton.setEnabled(canManageStaff && isStaffSelected);
}
private void addStaff() {
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_manage_staff")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You do not have permission to add staff members.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Proceed with staff addition logic
}
}
4.3 Dynamic Permission Checking
/**
* Example of dynamic permission checking in appointment booking
*/
private void bookNewAppointment() {
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_book_appointment")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You do not have permission to book appointments.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// For doctors, automatically select their own profile
Doctor selectedDoctor = null;
if (currentUser.getDoctorId() != null) {
// Doctor can only book appointments for themselves
for (Doctor doc : currentDoctors) {
if (doc.getDoctorId().equals(currentUser.getDoctorId())) {
selectedDoctor = doc;
break;
}
}
if (selectedDoctor == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"Your staff account's doctor ID is not linked to an active doctor profile. " +
"Please contact admin.", "Configuration Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
} else {
// Non-doctors (nurses/admins) can select any doctor
selectedDoctor = view.getSelectedDoctor(currentDoctors);
if (selectedDoctor == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"Please select a doctor first.", "Validation Error", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
}
// Continue with booking logic...
}
5. Permission Management System
5.1 Role-Specific Permission Implementation
Doctor Role Permissions
public class DoctorRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
switch (permission) {
case "can_access_appointments":
return true; // Doctors can view appointment schedules
case "can_mark_appointment_done":
return true; // Doctors can mark their appointments as completed
case "can_update_appointment":
return true; // Doctors can modify appointment details
case "can_access_patients":
return true; // Doctors can access patient records
case "can_add_appointment_notes":
return true; // Doctors can add medical notes and prescriptions
default:
return super.hasPermission(permission);
}
}
}
Nurse Role Permissions
public class NurseRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// Permissions nurses HAVE
Set<String> nursePermissions = Set.of(
"can_access_patients",
"can_access_appointments",
"can_generate_reports",
"can_book_appointment",
"can_cancel_appointment",
"can_update_appointment_reason"
);
if (nursePermissions.contains(permission)) {
return true;
}
// Permissions nurses explicitly DO NOT have
Set<String> restrictedPermissions = Set.of(
"can_delete_patient",
"can_delete_appointment",
"can_delete_bill",
"can_mark_appointment_done",
"can_access_billing",
"can_view_all_patients",
"can_manage_staff",
"can_manage_doctors"
);
if (restrictedPermissions.contains(permission)) {
return false;
}
return super.hasPermission(permission);
}
}
Admin Role Permissions
public class AdminRole extends UserRoleDecorator {
@Override
public boolean hasPermission(String permission) {
// Admins have all permissions - no restrictions
return true;
}
}
5.2 Context-Aware Permission Checking
/**
* Example of context-aware permission checking for appointment updates
*/
private void updatePrescription() {
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You do not have permission to update prescriptions.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
Appointment selectedAppointment = view.getSelectedAppointment(currentAppointments);
if (selectedAppointment == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"Please select an appointment to update prescription.",
"Warning", JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Additional context check: Only doctors can update their own appointment prescriptions
if (currentUser.getDoctorId() == null ||
!currentUser.getDoctorId().equals(selectedAppointment.getDoctorId())) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You can only update prescriptions for your own appointments.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Check appointment status
if ("Canceled".equalsIgnoreCase(selectedAppointment.getStatus())) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"Cannot update prescription for canceled appointments.",
"Invalid Operation", JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Proceed with prescription update
}
5.3 Permission Hierarchies and Combinations
/**
* Example showing how different roles interact with the same feature
*/
private void markSelectedAppointmentAsDone() {
if (!currentUser.hasPermission("can_mark_appointment_done")) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You do not have permission to mark appointments as done.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
Appointment selectedAppointment = view.getSelectedAppointment(currentAppointments);
if (selectedAppointment == null) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"Please select an appointment to mark as done.",
"Warning", JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Context-specific rules based on role
if (currentUser.getDoctorId() != null) {
// Doctors can only mark their own appointments as done
if (!currentUser.getDoctorId().equals(selectedAppointment.getDoctorId())) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(mainFrame,
"You can only mark your own appointments as done.",
"Access Denied", JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
return;
}
}
// Admins can mark any appointment as done (no additional restrictions)
// Status validation
if ("Done".equalsIgnoreCase(selectedAppointment.getStatus())) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(view,
"Appointment is already marked as Done.",
"Information", JOptionPane.INFORMATION_MESSAGE);
return;
}
// Proceed with marking appointment as done
}
6. Usage Scenarios
6.1 Scenario 1: Doctor Login and Permissions
// Login process for a doctor
AuthService authService = new AuthService();
IUser doctorUser = authService.login("dr_smith", "password123");
// Expected decoration chain: BaseUser → DoctorRole
// Doctor permissions available:
assertTrue(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_access_appointments"));
assertTrue(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_mark_appointment_done"));
assertTrue(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes"));
assertTrue(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_access_patients"));
// Doctor permissions NOT available:
assertFalse(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_book_appointment"));
assertFalse(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_delete_patient"));
assertFalse(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_manage_staff"));
assertFalse(doctorUser.hasPermission("can_access_billing"));
// Doctor-specific data available:
assertNotNull(doctorUser.getDoctorId()); // "D001"
assertEquals("Doctor", doctorUser.getRole());
assertEquals("dr_smith", doctorUser.getUsername());
6.2 Scenario 2: Nurse Login and Permissions
// Login process for a nurse
IUser nurseUser = authService.login("nurse_jane", "securepass");
// Expected decoration chain: BaseUser → NurseRole
// Nurse permissions available:
assertTrue(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_access_patients"));
assertTrue(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_access_appointments"));
assertTrue(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_book_appointment"));
assertTrue(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_cancel_appointment"));
assertTrue(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_update_appointment_reason"));
assertTrue(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_generate_reports"));
// Nurse permissions NOT available:
assertFalse(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_mark_appointment_done"));
assertFalse(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes"));
assertFalse(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_delete_patient"));
assertFalse(nurseUser.hasPermission("can_access_billing"));
// Nurse-specific data:
assertNull(nurseUser.getDoctorId()); // Nurses don't have doctor IDs
assertEquals("Nurse", nurseUser.getRole());
assertEquals("nurse_jane", nurseUser.getUsername());
6.3 Scenario 3: Admin Login and Permissions
// Login process for an admin
IUser adminUser = authService.login("admin_bob", "adminpass");
// Expected decoration chain: BaseUser → AdminRole
// Admin has ALL permissions:
assertTrue(adminUser.hasPermission("can_access_appointments"));
assertTrue(adminUser.hasPermission("can_delete_patient"));
assertTrue(adminUser.hasPermission("can_manage_staff"));
assertTrue(adminUser.hasPermission("can_manage_doctors"));
assertTrue(adminUser.hasPermission("can_access_billing"));
assertTrue(adminUser.hasPermission("can_process_payments"));
assertTrue(adminUser.hasPermission("any_permission_string"));
// Admin-specific data:
assertNull(adminUser.getDoctorId()); // Admins typically don't have doctor IDs
assertEquals("Admin", adminUser.getRole());
assertEquals("admin_bob", adminUser.getUsername());
6.4 Scenario 4: Permission-Based UI Updates
// Example of how UI elements are dynamically enabled/disabled
public class AppointmentController {
private void updateUIBasedOnPermissions() {
// Appointment booking - available to nurses and admins
view.bookAppointmentButton.setEnabled(
currentUser.hasPermission("can_book_appointment")
);
// Doctor management - admin only
boolean canManageDoctors = currentUser.hasPermission("can_manage_doctors");
view.addDoctorButton.setEnabled(canManageDoctors);
view.deleteDoctorButton.setEnabled(canManageDoctors);
// Doctor-specific view - available if user is a doctor OR has appointment access
view.viewScheduleButton.setEnabled(
currentUser.getDoctorId() != null ||
currentUser.hasPermission("can_access_appointments")
);
// Different buttons for different roles on same appointment
if (selectedAppointment != null) {
boolean isDoctor = currentUser.getDoctorId() != null;
boolean isOwner = isDoctor &&
currentUser.getDoctorId().equals(selectedAppointment.getDoctorId());
// Only doctors can update prescriptions on their own appointments
view.updatePrescriptionButton.setEnabled(
currentUser.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes") &&
isOwner
);
// Only nurses/admins can update appointment reasons
view.updateReasonButton.setEnabled(
currentUser.hasPermission("can_update_appointment_reason") &&
!isDoctor
);
}
}
}
7. Benefits & Trade-offs
7.1 Decorator Pattern Benefits
Flexible Permission Composition
- Multiple roles can be combined by stacking decorators
- New roles can be added without modifying existing code
- Permission logic is encapsulated within specific role classes
- Easy to add temporary or special permissions
Single Responsibility Principle
- Each role decorator focuses on specific permission sets
- Base user handles core user data without permission logic
- Clear separation between user identification and authorization
- Easy to modify individual role permissions
Open/Closed Principle
- System is open for extension (new roles) but closed for modification
- Existing role implementations remain unchanged when adding new roles
- Permission changes localized to specific role classes
- Easy to test individual permission sets
Runtime Flexibility
- User permissions can be modified during session if needed
- Multiple decorators can be applied to same user
- Context-aware permission checking supported
- Dynamic role assignment possible
7.2 Healthcare Domain Specific Benefits
Regulatory Compliance
- Clear audit trail of permission usage
- Role-based access control required by healthcare regulations
- Separation of clinical and administrative permissions
- Easy to demonstrate compliance with access control requirements
Patient Safety
- Prevents unauthorized access to patient data
- Ensures only qualified staff can perform medical procedures
- Clear boundaries between different healthcare roles
- Reduces risk of data breaches or unauthorized modifications
Operational Efficiency
- Staff can only access functions relevant to their role
- Reduced UI complexity by hiding irrelevant features
- Clear workflow separation between different staff types
- Minimizes training requirements for role-specific features
Scalability
- Easy to add new healthcare roles (e.g., Pharmacist, Lab Technician)
- Supports complex organizational hierarchies
- Can handle temporary role assignments or coverage situations
- Adapts to different healthcare facility structures
7.3 Trade-offs and Considerations
Complexity Management
- Multiple layers of decoration can make debugging difficult
- Permission checking logic distributed across multiple classes
- Need careful design to avoid permission conflicts
- Stack of decorators can impact performance
Testing Complexity
- Need to test all possible permission combinations
- Integration testing required for role interactions
- Mock objects needed for decorator chains
- Permission edge cases can be difficult to identify
Performance Considerations
- Method call overhead through decorator chain
- Permission checking happens frequently throughout application
- Memory overhead for decorator objects
- May need caching for frequently checked permissions
Maintenance Overhead
- Permission changes may require updates across multiple classes
- Need to maintain consistency between roles
- Documentation critical for understanding permission matrix
- Version control of permission changes becomes important
8. Testing & Validation
8.1 Unit Testing Role Decorators
@Test
public void testDoctorRolePermissions() {
// Arrange
BaseUser baseUser = new BaseUser("dr_test", "Doctor", "D001");
DoctorRole doctorRole = new DoctorRole(baseUser);
// Act & Assert - Doctor permissions
assertTrue(doctorRole.hasPermission("can_access_appointments"));
assertTrue(doctorRole.hasPermission("can_mark_appointment_done"));
assertTrue(doctorRole.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes"));
assertTrue(doctorRole.hasPermission("can_access_patients"));
// Act & Assert - Non-doctor permissions
assertFalse(doctorRole.hasPermission("can_book_appointment"));
assertFalse(doctorRole.hasPermission("can_delete_patient"));
assertFalse(doctorRole.hasPermission("can_manage_staff"));
// Act & Assert - Base user properties preserved
assertEquals("dr_test", doctorRole.getUsername());
assertEquals("Doctor", doctorRole.getRole());
assertEquals("D001", doctorRole.getDoctorId());
}
@Test
public void testNurseRolePermissions() {
// Arrange
BaseUser baseUser = new BaseUser("nurse_test", "Nurse", null);
NurseRole nurseRole = new NurseRole(baseUser);
// Act & Assert - Nurse permissions
assertTrue(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_access_patients"));
assertTrue(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_book_appointment"));
assertTrue(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_cancel_appointment"));
assertTrue(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_update_appointment_reason"));
// Act & Assert - Restricted permissions
assertFalse(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_mark_appointment_done"));
assertFalse(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_add_appointment_notes"));
assertFalse(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_delete_patient"));
assertFalse(nurseRole.hasPermission("can_access_billing"));
}
@Test
public void testAdminRolePermissions() {
// Arrange
BaseUser baseUser = new BaseUser("admin_test", "Admin", null);
AdminRole adminRole = new AdminRole(baseUser);
// Act & Assert - Admin has all permissions
assertTrue(adminRole.hasPermission("can_access_appointments"));
assertTrue(adminRole.hasPermission("can_delete_patient"));
assertTrue(adminRole.hasPermission("can_manage_staff"));
assertTrue(adminRole.hasPermission("can_access_billing"));
assertTrue(adminRole.hasPermission("any_permission"));
assertTrue(adminRole.hasPermission("non_existent_permission"));
}
8.2 Integration Testing with Controllers
@Test
public void testAppointmentControllerWithDoctorUser() {
// Arrange
IUser doctorUser = new DoctorRole(new BaseUser("dr_test", "Doctor", "D001"));
AppointmentController controller = new AppointmentController(view, mainFrame, doctorUser);
// Act
controller.applyPermissions();
// Assert - Doctor-specific UI states
assertTrue(view.viewScheduleButton.isEnabled()); // Doctor can view their schedule
assertFalse(view.bookAppointmentButton.isEnabled()); // Doctor cannot book appointments
assertTrue(view.viewAllAppointmentsButton.isEnabled()); // Doctor can view appointments
assertFalse(view.addDoctorButton.isEnabled()); // Doctor cannot manage other doctors
}
@Test
public void testPatientControllerWithNurseUser() {
// Arrange
IUser nurseUser = new NurseRole(new BaseUser("nurse_test", "Nurse", null));
PatientController controller = new PatientController(view, mainFrame, nurseUser);
// Act
controller.initController();
// Assert - Nurse-specific UI states
assertFalse(view.viewAllButton.isEnabled()); // Nurse cannot view all patients
// Nurse can access individual patients but not perform bulk operations
}
@Test
public void testStaffControllerWithAdminUser() {
// Arrange
IUser adminUser = new AdminRole(new BaseUser("admin_test", "Admin", null));
StaffController controller = new StaffController(view, mainFrame, adminUser);
// Act
controller.applyPermissions();
// Assert - Admin has full access
assertTrue(view.addButton.isEnabled());
assertTrue(view.updateButton.isEnabled() || !isStaffSelected());
assertTrue(view.deleteButton.isEnabled() || !isStaffSelected());
assertTrue(view.refreshStaffButton.isEnabled());
}
8.3 Security Testing
@Test
public void testUnauthorizedAccess() {
// Test that users without permissions cannot access restricted functions
IUser nurseUser = new NurseRole(new BaseUser("nurse_test", "Nurse", null));
// Attempt unauthorized operations
AppointmentController controller = new AppointmentController(view, mainFrame, nurseUser);
// These should fail with appropriate error messages
assertThrows(SecurityException.class, () -> {
controller.deleteDoctor(); // Nurse cannot delete doctors
});
PatientController patientController = new PatientController(view, mainFrame, nurseUser);
assertThrows(SecurityException.class, () -> {
patientController.deletePatient(); // Nurse cannot delete patients
});
}
@Test
public void testPermissionEscalation() {
// Test that users cannot escalate their permissions
BaseUser baseUser = new BaseUser("test_user", "Unknown", null);
// Base user should have no permissions
assertFalse(baseUser.hasPermission("can_access_patients"));
assertFalse(baseUser.hasPermission("can_delete_patient"));
assertFalse(baseUser.hasPermission("admin_permission"));
// Adding unknown role should not grant permissions
// (This would be handled by the factory method returning base user)
}
8.4 Performance Testing
@Test
public void testPermissionCheckingPerformance() {
// Arrange
IUser doctorUser = new DoctorRole(new BaseUser("dr_test", "Doctor", "D001"));
int iterations = 100000;
// Act
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
doctorUser.hasPermission("can_access_appointments");
doctorUser.hasPermission("can_delete_patient");
doctorUser.hasPermission("can_manage_staff");
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
// Assert
long durationMs = (endTime - startTime) / 1_000_000;
assertTrue("Permission checking should be fast", durationMs < 100);
System.out.println(String.format("Permission checking: %d iterations in %d ms",
iterations * 3, durationMs));
}
Conclusion
The Decorator pattern implementation for medical staff roles and permissions demonstrates a sophisticated approach to access control in healthcare systems. The pattern successfully addresses the complex requirements of role-based permissions while maintaining flexibility and extensibility.
Key Achievements
- Flexible Role Management: Successfully implements a dynamic permission system that can adapt to different healthcare organizational structures
- Security Compliance: Provides robust access control mechanisms essential for healthcare data protection and regulatory compliance
- Extensible Architecture: Easy addition of new roles without modifying existing code, supporting evolving healthcare requirements
- Clear Separation of Concerns: Clean separation between user identification, role assignment, and permission checking
- Context-Aware Permissions: Supports complex permission scenarios where access depends on ownership, status, or other contextual factors
Real-World Healthcare Impact
The Decorator pattern proves particularly valuable in healthcare contexts where:
- Regulatory Compliance requires strict role-based access control with audit capabilities
- Patient Safety depends on ensuring only qualified staff can access or modify sensitive medical data
- Operational Efficiency benefits from role-appropriate UI and functionality exposure
- Staff Management needs flexible permission assignment for different healthcare roles and temporary assignments
- System Integration requires clear permission boundaries for interfacing with external healthcare systems
Pattern Benefits Realized
The implementation successfully demonstrates how the Decorator pattern can:
- Enable dynamic composition of permissions without complex inheritance hierarchies
- Support fine-grained access control with role-specific and context-aware permissions
- Facilitate easy testing and validation of individual role permissions
- Provide clear audit trails for security and compliance requirements
- Maintain clean separation between user authentication and authorization concerns
The medical staff permission system provides a robust foundation for secure healthcare application access while maintaining the flexibility needed for complex healthcare organizational structures and evolving regulatory requirements.
Document Status: Part D Complete
Next: Part E: Generating Medical Reports - Visitor Pattern